Page 142 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 142
2
126 Automobile mechanical and electrical systems
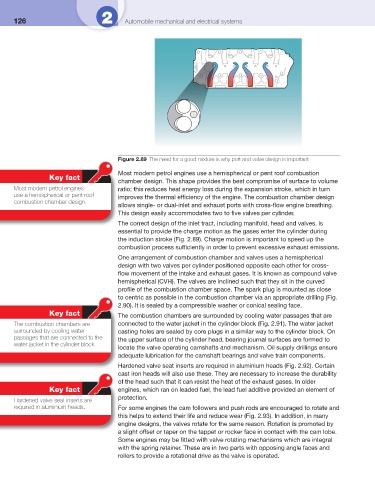
Figure 2.89 The need for a good mixture is why port and valve design is important
Most modern petrol engines use a hemispherical or pent roof combustion
Key fact
chamber design. This shape provides the best compromise of surface to volume
Most modern petrol engines ratio; this reduces heat energy loss during the expansion stroke, which in turn
use a hemispherical or pent roof improves the thermal effi ciency of the engine. The combustion chamber design
combustion chamber design.
allows single- or dual-inlet and exhaust ports with cross-fl ow engine breathing.
This design easily accommodates two to fi ve valves per cylinder.
The correct design of the inlet tract, including manifold, head and valves, is
essential to provide the charge motion as the gases enter the cylinder during
the induction stroke ( Fig. 2.89 ). Charge motion is important to speed up the
combustion process suffi ciently in order to prevent excessive exhaust emissions.
One arrangement of combustion chamber and valves uses a hemispherical
design with two valves per cylinder positioned opposite each other for cross-
fl ow movement of the intake and exhaust gases. It is known as compound valve
hemispherical (CVH). The valves are inclined such that they sit in the curved
profi le of the combustion chamber space. The spark plug is mounted as close
to centric as possible in the combustion chamber via an appropriate drilling ( Fig.
2.90 ). It is sealed by a compressible washer or conical sealing face.
Key fact The combustion chambers are surrounded by cooling water passages that are
The combustion chambers are connected to the water jacket in the cylinder block ( Fig. 2.91 ). The water jacket
surrounded by cooling water casting holes are sealed by core plugs in a similar way to the cylinder block. On
passages that are connected to the the upper surface of the cylinder head, bearing journal surfaces are formed to
water jacket in the cylinder block.
locate the valve operating camshafts and mechanism. Oil supply drillings ensure
adequate lubrication for the camshaft bearings and valve train components.
Hardened valve seat inserts are required in aluminium heads ( Fig. 2.92 ). Certain
cast iron heads will also use these. They are necessary to increase the durability
of the head such that it can resist the heat of the exhaust gases. In older
Key fact engines, which ran on leaded fuel, the lead fuel additive provided an element of
protection.
Hardened valve seat inserts are
required in aluminium heads. For some engines the cam followers and push rods are encouraged to rotate and
this helps to extend their life and reduce wear ( Fig. 2.93 ). In addition, in many
engine designs, the valves rotate for the same reason. Rotation is promoted by
a slight offset or taper on the tappet or rocker face in contact with the cam lobe.
Some engines may be fi tted with valve rotating mechanisms which are integral
with the spring retainer. These are in two parts with opposing angle faces and
rollers to provide a rotational drive as the valve is operated.