Page 237 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 237
2
Engine systems 221
5
1
A
6
2
3
4
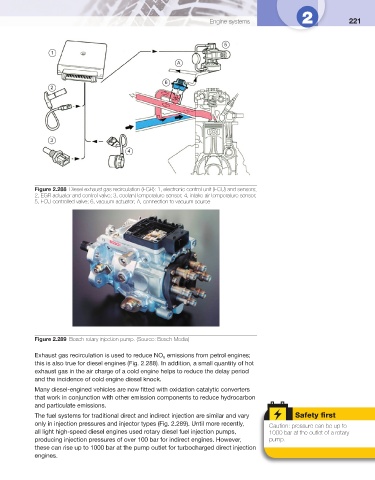
Figure 2.288 Diesel exhaust gas recirculation (EGR): 1, electronic control unit (ECU) and sensors;
2, EGR actuator and control valve; 3, coolant temperature sensor; 4, intake air temperature sensor;
5, ECU controlled valve; 6, vacuum actuator; A, connection to vacuum source
Figure 2.289 Bosch rotary injection pump. (Source: Bosch Media)
Exhaust gas recirculation is used to reduce NO emissions from petrol engines;
x
this is also true for diesel engines ( Fig. 2.288 ). In addition, a small quantity of hot
exhaust gas in the air charge of a cold engine helps to reduce the delay period
and the incidence of cold engine diesel knock.
Many diesel-engined vehicles are now fi tted with oxidation catalytic converters
that work in conjunction with other emission components to reduce hydrocarbon
and particulate emissions.
The fuel systems for traditional direct and indirect injection are similar and vary Safety fi rst
only in injection pressures and injector types ( Fig. 2.289 ). Until more recently, Caution: pressure can be up to
all light high-speed diesel engines used rotary diesel fuel injection pumps, 1000 bar at the outlet of a rotary
producing injection pressures of over 100 bar for indirect engines. However, pump.
these can rise up to 1000 bar at the pump outlet for turbocharged direct injection
engines.