Page 262 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 262
2
246 Automobile mechanical and electrical systems
1 2 3
S
N
4
5
6
Figure 2.329 Inductive sensor: 1, magnet; 2, cover; 3, engine; 4, core; 5, winding; 6, missing
tooth
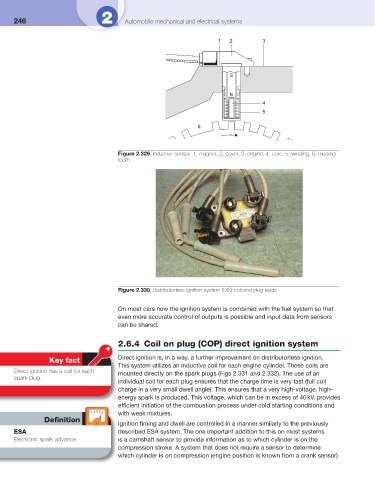
Figure 2.330 Distributorless ignition system (DIS) coil and plug leads
On most cars now the ignition system is combined with the fuel system so that
even more accurate control of outputs is possible and input data from sensors
can be shared.
2.6.4 Coil on plug (COP) direct ignition system
Direct ignition is, in a way, a further improvement on distributorless ignition.
Key fact
This system utilizes an inductive coil for each engine cylinder. These coils are
Direct ignition has a coil for each mounted directly on the spark plugs ( Figs 2.331 and 2.332 ). The use of an
spark plug.
individual coil for each plug ensures that the charge time is very fast (full coil
charge in a very small dwell angle). This ensures that a very high-voltage, high-
energy spark is produced. This voltage, which can be in excess of 40 kV, provides
effi cient initiation of the combustion process under cold starting conditions and
with weak mixtures.
Defi nition
Ignition timing and dwell are controlled in a manner similarly to the previously
ESA described ESA system. The one important addition to this on most systems
Electronic spark advance. is a camshaft sensor to provide information as to which cylinder is on the
compression stroke. A system that does not require a sensor to determine
which cylinder is on compression (engine position is known from a crank sensor)