Page 68 - Basic physical chemistry for the atmospheric sciences
P. 68
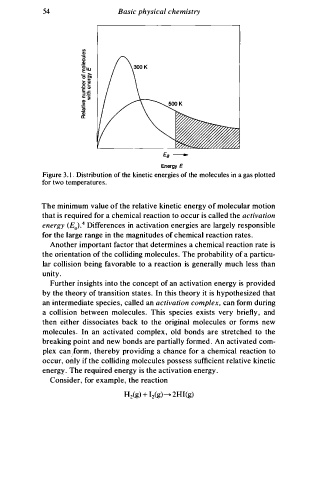
54 Basic physical chemistry
Ea -
Energy E
Figure 3 . I . Distribution of the kinetic energies of the molecules in a gas plotted
for two temperatures.
The minimum value of the relative kinetic energy of molecular motion
that is required for a chemical reaction to occur is called the activation
4
energy (Ea) . Differences in activation energies are largely responsible
s
for the large range in the magnitudes of chemical reaction rate .
Another important factor that determines a chemical reaction rate is
s
the orientation of the colliding molecule . The probability of a particu
lar collision being favorable to a reaction is generally much less than
unity.
Further insights into the concept of an activation energy is provided
by the theory of transition states. In this theory it is hypothesized that
an intermediate species, called an activation complex, can form during
a collision between molecules. This species exists very briefly, and
then either dissociates back to the original molecules or forms new
x
molecules. In an activated comple , old bonds are stretched to the
breaking point and new bonds are partially formed. An activated com
plex can form , thereby providing a chance for a chemical reaction to
occur, only if the colliding molecules possess sufficient relative kinetic
energy. The required energy is the activation energy.
Consider, for example, the reaction