Page 62 - Basics of MATLAB and Beyond
P. 62
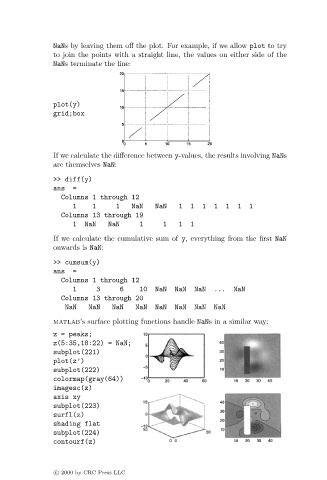
NaNs by leaving them off the plot. For example, if we allow plot to try
to join the points with a straight line, the values on either side of the
NaNs terminate the line:
plot(y)
grid;box
If we calculate the difference between y-values, the results involving NaNs
are themselves NaN:
>> diff(y)
ans =
Columns 1 through 12
1 1 1 NaN NaN 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Columns 13 through 19
1 NaN NaN 1 1 1 1
If we calculate the cumulative sum of y, everything from the first NaN
onwards is NaN:
>> cumsum(y)
ans =
Columns 1 through 12
1 3 6 10 NaN NaN NaN ... NaN
Columns 13 through 20
NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
matlab’s surface plotting functions handle NaNs in a similar way:
z = peaks;
z(5:35,18:22) = NaN;
subplot(221)
plot(z’)
subplot(222)
colormap(gray(64))
imagesc(z)
axis xy
subplot(223)
surfl(z)
shading flat
subplot(224)
contourf(z)
c 2000 by CRC Press LLC