Page 101 - Battery Reference Book
P. 101
2/18 Guidelines to battery selection
life and indefinite shelf life in any state of charge with-
out electrode deterioration are advantageous. They are
- particularly suitable for trickle charge uses such as
220
emergency lighting.
210-
200 -
-
190 2.2.2 Nickel-cadmium batteries
180 - The nickel-cadmium battery is mechanically rugged
170- and long lived. In addition it has excellent low-
160 - temperature characteristics and can be hermetically
G 150- sealed. Cost, however, is higher than for either the
E
2 140- lead-acid or the nickel-zinc battery and, by compar-
r:
130- ison, its capacity on light drain in terms of watt hours
1 per kilogram is also poorer than for nickel-zinc.
.-
5 120-
UI For many everyday batteries, the choice is still
5 110-
-0 between the lead-acid and the nickel-cadmium sys-
5 100- tems, rather than the more recently developed systems
al
fi 90- discussed below.
80 - Each of these two main types of battery has its own
70 - advantages and the choice between nickel-cadmium
and lead-acid batteries depends very much on the
/ particular application and on the performance charac-
50- / teristics required.
/
40- / In addition to these two types of battery, there are
30 - several others which, because of their higher cost, are
20 - not used as extensively, but are nevertheless of direct
interest in particular fields. This is because of their out-
10 - standing performance characteristics in certain special-
, 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
ized applications, e.g. silver-zinc and silver-cadmium
batteries.
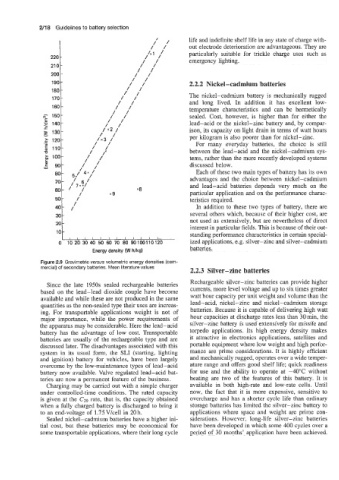
Figure 2.9 Gravimetric versus volumetric energy densities (com-
mercial) of secondary batteries. Mean literature values
2.2.3 Silver-zinc batteries
Rechargeable silver-zinc batteries can provide higher
Since the late 1950s sealed rechargeable batteries
based on the lead-lead dioxide couple have become currents, more level voltage and up to six times greater
available and while these are not produced in the same watt hour capacity per unit weight and volume than the
quantities as the non-sealed type their uses are increas- lead-acid, nickel-zinc and nickel-cadmium storage
ing. For transportable applications weight is not of batteries. Because it is capable of delivering high watt
major importance, while the power requirements of hour capacities at discharge rates less than 30 min, the
the apparatus may be considerable. Here the lead-acid silver-zinc battery is used extensively for missile and
battery has the advantage of low cost. Transportable torpedo applications. Its high energy density makes
batteries are usually of the rechargeable type and are it attractive in electronics applications, satellites and
discussed later. The disadvantages associated with this portable equipment where low weight and high perfor-
system in its usual form, the SLI (starting, lighting mance are prime considerations. It is highly efficient
and ignition) battery for vehicles, have been largely and mechanically rugged, operates over a wide temper-
overcome by the low-maintenance types of lead-acid ature range and offers good shelf life; quick readiness
battery now available. Valve regulated lead-acid bat- for use and the ability to operate at -40°C without
teries are now a permanent feature of the business. heating are two of the features of this battery. It is
Charging may be carried out with a simple charger available in both high-rate and low-rate cells. Until
under controlled-time conditions. The rated capacity now, the fact that it is more expensive, sensitive to
is given at the C20 rate, that is, the capacity obtained overcharge and has a shorter cycle life than ordinary
when a fully charged battery is discharged to bring it storage batteries has limited the silver-zinc battery to
to an end-voltage of 1.75 Vlcell in 20 h. applications where space and weight are prime con-
Sealed nickel-cadmium batteries have a higher ini- siderations. However, long-life silver-zinc batteries
tial cost, but these batteries may be economical for have been developed in which some 400 cycles over a
some transportable applications, where their long cycle period of 30 months’ application have been achieved.