Page 316 - Battery Reference Book
P. 316
Lithium alloy thermal batteries 27/13
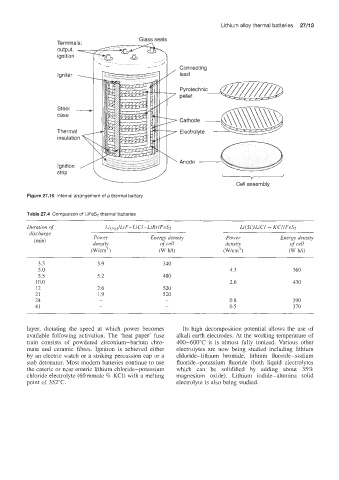
Connecting
lead
pellet -Q7/D
Pyrotechnic
Cathode -
Anode
Y
Cell assembly
Figure 27.16 internal arrangement of a thermal battery
Table 27.4 Comparison of LiFeS? thermal batteries
Duration of Li(llqjLzF-LiCl -LiBr/FeSz Li(Si)lLiCl - KCllFeS2
discharge Power Energy density Power Energy density
(min) density of cell density of cell
(W/cm3) (W w (Wicm3) (W w
3.5 5.9 340
5.0 4.3 360
5.5 5.2 480
10.0 2.6 430
12 2.6 520
21 1.9 520
24 0.8 390
41 0.5 370
layer, dictating the speed at which power becomes Its high decomposition potential allows the use of
available following activation. The 'heat paper' fuse alkali earth electrodes. At the working temperature of
train consists of powdered zirconium-barium chro- 400-600°C it is almost fully ionized. Various other
mate and ceramic fibres. Ignition is achieved either electrolytes are now being studied including lithium
by an electric watch or a striking percussion cap or a chloride-lithium bromide, lithium fluoride- sodium
stab detonator. Most modern batteries continue to use fluoride-potassium fluoride (both liquid electrolytes
the enteric or near enteric lithium chloride-potassium which can be solidified by adding about 35%
chloride electrolyte (60 mmole % KC1) with a melting magnesium oxide). Lithium iodide-alumina solid
point of 352°C. electrolyte is also being studied.