Page 86 - Battery Reference Book
P. 86
s
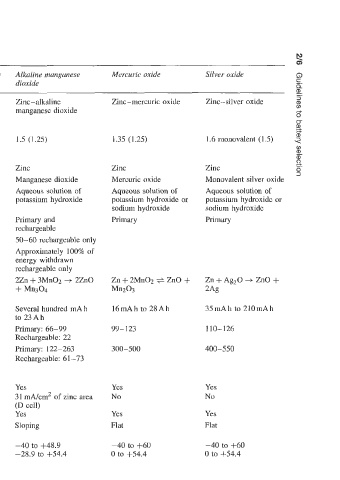
Table 2.2 Principal types of dry battery and average characteristics
Common name Carbon-zinc Carbon-zinc (zinc chloride) Alkaline manganese Mercuric oxide Silver oxide f
dioxide
Q
_.
(D
Electrochemical system Zinc-manganese Zinc-manganese dioxide Zinc-alkaline Zinc-mercuric oxide Zinc-silver oxide 3
8
dioxide (usually called manganese dioxide a
Leclanchk or 0-
carbon-zinc) 2
Voltage per cell (average 1.5 (1.2) 1.5 (1.2) 1.5 (1.25) 1.35 (1.25) 1.6 monovalent (1.5) 2
on-load voltage in
parentheses) (V)
Negative electrode Zinc Zinc Zinc Zinc
Positive electrode Manganese dioxide Manganese dioxide Manganese dioxide Mercuric oxide
Electrolyte Aqueous solution of Aqueous solution of zinc Aqueous solution of Aqueous solution of Aqueous solution of
ammonium chloride and chloride potassium hydroxide potassium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide or
zinc chloride sodium hydroxide sodium hydroxide
Primary Primary Primary and Primary Primary
rechargeable
Number of cycles 10-20 10-20 50-60 rechargeable only
Input if rechargeable Approximately 100% of
energy withdrawn
rechargeable only
Overall equation of 2MnO2 + 2NH4Cl + Zn 8MnO2 + 4Zn + ZnCl2 + 2Zn + 3Mn02 3 2Zn0
reaction + ZnC12.2NH3 + H20 9Hzo + 8Mn00H -I- + Mn304
+ Mn203 ZnCl2 .4ZnOSH20
Typical commercial 60mAh to 30Ah Several hundred mA h to Several hundred mA h 16mAh to 28Ah 35mAh to 2lOmAh
service capacity 9Ah to 23Ah
Commercial energy 55-77 88 Primary: 66-99 99- I23 110-126
density (Wkg) Rechargeable: 22
Commercial energy 120-152 183 Primary: 122-263 300-500 400-550
density (W/dm3) Rechargeable: 61 -73
Practical current drain
rates:
Pulse Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
High (>50mA) 15 mA/cm2 of zinc area 23 mA/cm2 of zinc area 31 mA/cm2 of zinc area No No
(D cell) (D cell) (D cell)
Low (40mA) Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Discharge curve shape Sloping Sloping Sloping Flat Flat
Temperature range (“C):
Storage -40 to +48 -40 to +71.1 -40 to +48.9 -40 to +60 -40 to +60
Operation -6.7 to +54.4 -17.8 to +71.1 -28.9 to 444.4 0 to +54.4 0 to +54.4