Page 114 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 114
BooleanAlgebra rn 95
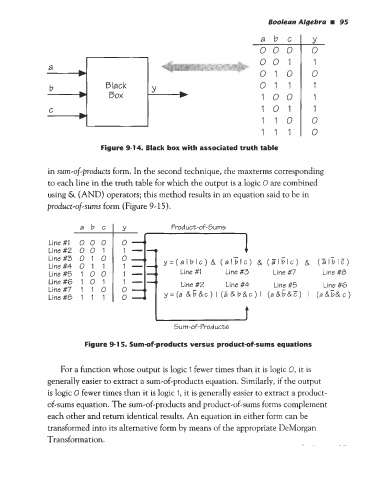
abc Y
000 0
00 1 1
a
b 010 0
b Black Y 01 1 1
b. Box b 100 1
c 101 1
110 0
1 1 1 0
Figure 9-14. Black box with associated truth table
in sum-of+roducts form. In the second technique, the maxterms corresponding
to each line in the truth table for which the output is a logic O are combined
using & (AND) operators; this method results in an equation said to be in
product-of-sums form (Figure 9- 15).
Product-of-Sums
Line#2 0 0 1
Line#3 0 1 0 y=(alblc) & (alblc) & (zIFI~) & (ZI~IE)
Line#4 0 1 1
Line#5 1 0 0 Line #I Line #3 Line #7 Line #8
Line#6 1 0 1 Line #2 Line #4 Line #5 Line #6
y=(a &6&c) 1 (Z&b&c)I (a&b&F) I (a&b&c)
t
5 u rn - of - Prod u et5
Figure 9-1 5. Sum-of-products versus product-of-sums equations
it
For a function whose output is logic I fewer times than it is logic 0, is
generally easier to extract a sum-of-products equation. Similarly, if the output
is logic O fewer times than it is logic I, it is generally easier to extract a product-
of-sums equation. The sum-of-products and product-of-sums forms complement
each other and return identical results. An equation in either form can be
transformed into its alternative form by means of the appropriate DeMorgan
Transformat ion.