Page 27 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 27
12 K. DANG VAN. A. BIGNONNET AND JTL. FAYARD
inducing a multiaxial state at the hot spots. This unique fatigue design curve is limited in its
upper part by the plastic yield stress of the material.
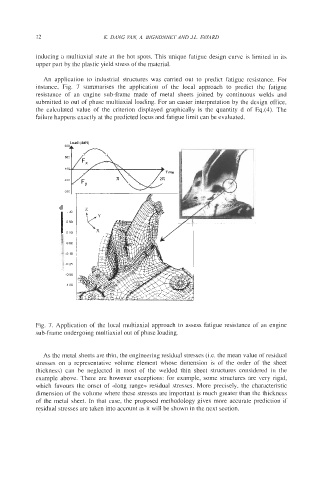
An application to industrial structures was carried out to predict fatigue resistance. For
instance, Fig. 7 summarises the application of the local approach to predict the fatigue
resistance of an engine sub-frame made of metal sheets joined by continuous welds and
submitted to out of phase multiaxial loading. For an easier interpretation by the design office,
the calculated value of the criterion displayed graphically is the quantity d of Eq.(4). The
failure I
Fig. 7. Application of the local multiaxial approach to assess fatigue resistance of an engine
sub-frame undergoing multiaxial out of phase loading.
As the metal sheets are thin, the engineering residual stresses (Le. the mean value of residual
stresses on a representative volume element whose dimension is of the order of the sheet
thickness) can be neglected in most of the welded thin sheet structures considered in the
example above. There are however exceptions: for example, some structures are very rigid,
which favours the onset of dong range,, residual stresses. More precisely, the characteristic
dimension of the volume where these stresses are important is much greater than the thickness
of the metal sheet. In that case, the proposed methodology gives more accurate prediction if
residual stresses are taken into account as it will be shown in the next section.