Page 441 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 441
I +
A Damage Model for Estimating Low Cycle Fatigue Lives Under Nonproportional Multiarial Loading 425
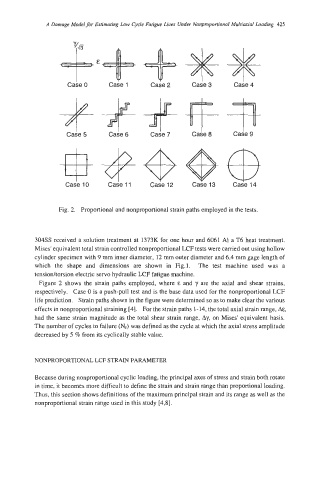
Case 0 Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 Case 4
case 5 Caie 6 Ca$e 8 Cade 9
Case IO Case 11 Case 12 Case 13 Case 14
Fig. 2. Proportional and nonproportional strain paths employed in the tests.
304SS received a solution treatment at 1373K for one hour and 6061 AI a T6 heat treatment.
Mises' equivalent total strain controlled nonproportional LCF tests were carried out using hollow
cylinder specimen with 9 mm inner diameter, 12 mm outer diameter and 6.4 mm gage length of
which the shape and dimensions are shown in Fig.1. The test machine used was a
tension/torsion electric servo hydraulic LCF fatigue machine.
Figure 2 shows the strain paths employed, where E and y are the axial and shear strains,
respectively. Case 0 is a push-pull test and is the base data used for the nonproportional LCF
life prediction. Strain paths shown in the figure were determined so as to make clear the various
effects in nonproportional straining [4]. For the strain paths 1-14, the total axial strain range, A&,
had the same strain magnitude as the total shear strain range, Ay, on Mises' equivalent basis.
The number of cycles to failure (Nf) was defined as the cycle at which the axial stress amplitude
decreased by 5 % from its cyclically stable value.
NONPROPORTIONAL LCF STRAIN PARAMETER
Because during nonproportional cyclic loading, the principal axes of stress and strain both rotate
in time, it becomes more difficult to define the strain and strain range than proportional loading.
Thus, this section shows definitions of the maximum principal strain and its range as well as the
nonproportional strain range used in this study [4,8].