Page 116 - Biobehavioral Resilence to Stress
P. 116
Adaptation to Stress 93
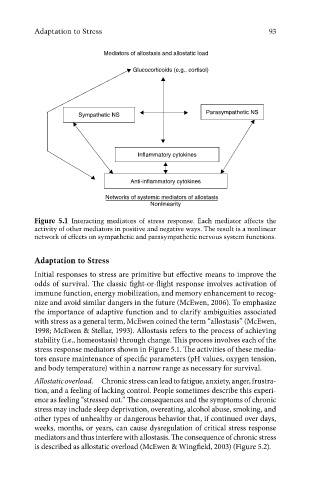
Mediators of allostasis and allostatic load
Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol)
Parasympathetic NS
Sympathetic NS
Inflammatory cytokines
Anti-inflammatory cytokines
Networks of systemic mediators of allostasis
Nonlinearity
Figure 5.1 Interacting mediators of stress response. Each mediator affects the
activity of other mediators in positive and negative ways. The result is a nonlinear
network of effects on sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system functions.
Adaptation to Stress
Initial responses to stress are primitive but effective means to improve the
odds of survival. The classic fi ght-or-flight response involves activation of
immune function, energy mobilization, and memory enhancement to recog-
nize and avoid similar dangers in the future (McEwen, 2006). To emphasize
the importance of adaptive function and to clarify ambiguities associated
with stress as a general term, McEwen coined the term “allostasis” (McEwen,
1998; McEwen & Stellar, 1993). Allostasis refers to the process of achieving
stability (i.e., homeostasis) through change. This process involves each of the
stress response mediators shown in Figure 5.1. The activities of these media-
tors ensure maintenance of specifi c parameters (pH values, oxygen tension,
and body temperature) within a narrow range as necessary for survival.
Allostatic overload. Chronic stress can lead to fatigue, anxiety, anger, frustra-
tion, and a feeling of lacking control. People sometimes describe this experi-
ence as feeling “stressed out.” The consequences and the symptoms of chronic
stress may include sleep deprivation, overeating, alcohol abuse, smoking, and
other types of unhealthy or dangerous behavior that, if continued over days,
weeks, months, or years, can cause dysregulation of critical stress response
mediators and thus interfere with allostasis. The consequence of chronic stress
is described as allostatic overload (McEwen & Wingfield, 2003) (Figure 5.2).
12/17/2007 3:27:52 PM
CRC_71777_Ch005.indd 93 12/17/2007 3:27:52 PM
CRC_71777_Ch005.indd 93