Page 113 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 113
5.1 Introduction 89
Besides hydroxylation reaction, P450s catalyze many other oxidative processes
such as epoxidation, dealkylation, carbon–carbon bond cleavage and formation,
decarboxylation, dimerization, dehydration, nitrogen and sulfur oxidations [8], as
well as unusual reactions such as ring expansion, contraction, and coupling [9].
Most of these chemical reactions can be explained on the basis of a classical
P450 catalytic cycle involving the high-valent iron–oxygen complex Compound I
(Scheme 5.2) [10].
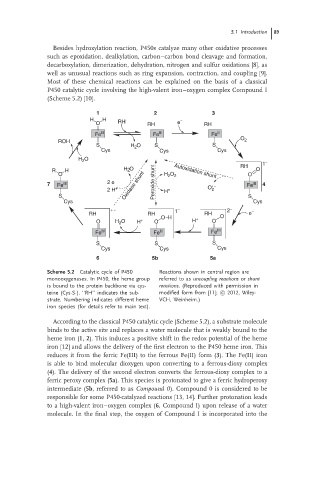
1 2 3
H H RH −
O RH e RH
Fe III Fe III Fe II
O 2
ROH
S H 2 O S S
Cys Cys Cys
H 2 O
1 −
RH
R H H 2 O Autoxidation shunt O
O H 2 O 2 O
7 Fe III 2 e − Oxidase shunt Peroxide shunt − Fe III 4
2 H + H + O 2
S S
Cys Cys
+ 1 − 2 − −
RH RH RH e
O H + O
O H 2 O H + O H O
Fe IV Fe III Fe III
S S S
Cys Cys Cys
6 5b 5a
Scheme 5.2 Catalytic cycle of P450 Reactions shown in central region are
monooxygenases. In P450, the heme group referred to as uncoupling reactions or shunt
is bound to the protein backbone via cys- reactions. (Reproduced with permission in
teine (Cys-S-). ‘‘RH’’ indicates the sub- modified form from [11]; c 2012, Wiley-
strate. Numbering indicates different heme VCH, Weinheim.)
iron species (for details refer to main text).
According to the classical P450 catalytic cycle (Scheme 5.2), a substrate molecule
binds to the active site and replaces a water molecule that is weakly bound to the
heme iron (1, 2). This induces a positive shift in the redox potential of the heme
iron [12] and allows the delivery of the first electron to the P450 heme iron. This
reduces it from the ferric Fe(III) to the ferrous Fe(II) form (3). The Fe(II) iron
is able to bind molecular dioxygen upon converting to a ferrous-dioxy complex
(4). The delivery of the second electron converts the ferrous-dioxy complex to a
ferric peroxy complex (5a). This species is protonated to give a ferric hydroperoxy
intermediate (5b, referred to as Compound 0). Compound 0 is considered to be
responsible for some P450-catalyzed reactions [13, 14]. Further protonation leads
to a high-valent iron–oxygen complex (6, Compound I) upon release of a water
molecule. In the final step, the oxygen of Compound I is incorporated into the