Page 172 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 172
148 6 Chemo-Enzymatic Cascade Reactions for the Synthesis of Glycoconjugates
Acetate
Acetyl P i
a
ATP
UMP UDP
b
Acetyl P i
a
Acetate
UTP
Chemical synthesis OH OH
HO HO
HO c HO
OH OH
OPO 3 2− PP i OUDP
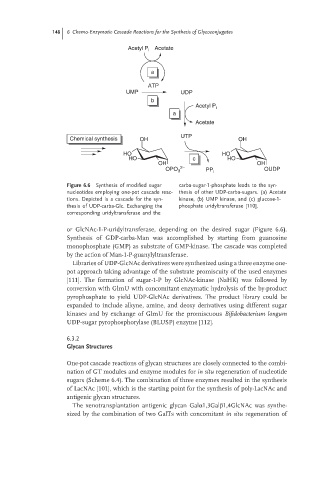
Figure 6.6 Synthesis of modified sugar carba-sugar-1-phosphate leads to the syn-
nucleotides employing one-pot cascade reac- thesis of other UDP-carba-sugars. (a) Acetate
tions. Depicted is a cascade for the syn- kinase, (b) UMP kinase, and (c) glucose-1-
thesis of UDP-carba-Glc. Exchanging the phosphate uridyltransferase [110].
corresponding uridyltransferase and the
or GlcNAc-1-P-uridyltransferase, depending on the desired sugar (Figure 6.6).
Synthesis of GDP-carba-Man was accomplished by starting from guanosine
monophosphate (GMP) as substrate of GMP-kinase. The cascade was completed
by the action of Man-1-P-guanylyltransferase.
Libraries of UDP-GlcNAc derivatives were synthesized using a three enzyme one-
pot approach taking advantage of the substrate promiscuity of the used enzymes
[111]. The formation of sugar-1-P by GlcNAc-kinase (NaHK) was followed by
conversion with GlmU with concomitant enzymatic hydrolysis of the by-product
pyrophosphate to yield UDP-GlcNAc derivatives. The product library could be
expanded to include alkyne, amine, and deoxy derivatives using different sugar
kinases and by exchange of GlmU for the promiscuous Bifidobacterium longum
UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase (BLUSP) enzyme [112].
6.3.2
Glycan Structures
One-pot cascade reactions of glycan structures are closely connected to the combi-
nation of GT modules and enzyme modules for in situ regeneration of nucleotide
sugars (Scheme 6.4). The combination of three enzymes resulted in the synthesis
of LacNAc [101], which is the starting point for the synthesis of poly-LacNAc and
antigenic glycan structures.
The xenotransplantation antigenic glycan Galα1,3Galβ1,4GlcNAc was synthe-
sized by the combination of two GalTs with concomitant in situ regeneration of