Page 205 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 205
8.2 The Tools 181
mostly employed for catalyzing the selective hydrolysis of acylated compounds,
they are often able to accept other nucleophiles instead of water, such as alcohols or
amines yielding an ester or amide, respectively, when starting from a suitable acyl
precursor [14, 15]. In particular, this precursor is usually designed to irreversibly
transfer its acyl moiety to the respective nucleophile, hence to permit the reaction
to reach its completion and to be kinetically stable under the reaction conditions
in the absence of the catalyst in order to avoid spontaneous nonselective side
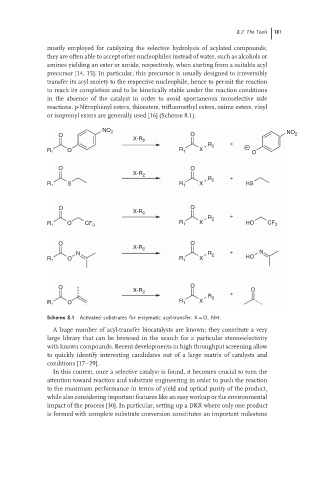
reactions. p-Nitrophenyl esters, thioesters, trifluoroethyl esters, oxime esters, vinyl
or isoprenyl esters are generally used [16] (Scheme 8.1).
NO 2
O O NO 2
X-R 2
R 2 +
R 1 O R 1 X O
O O
X-R 2
R 2 +
R 1 S R 1 X HS
O O
X-R 2
+
R 2
R 1 O CF 3 R 1 X HO CF 3
O O
X-R 2
N R 2 + N
R 1 O R 1 X HO
O O
X-R 2 O
R 2 +
R 1 O R 1 X
Scheme 8.1 Activated substrates for enzymatic acyl-transfer. X = O, NH.
A huge number of acyl-transfer biocatalysts are known: they constitute a very
large library that can be browsed in the search for a particular stereoselectivity
with known compounds. Recent developments in high throughput screening allow
to quickly identify interesting candidates out of a large matrix of catalysts and
conditions [17–29].
In this context, once a selective catalyst is found, it becomes crucial to turn the
attention toward reaction and substrate engineering in order to push the reaction
to the maximum performance in terms of yield and optical purity of the product,
while also considering important features like an easy workup or the environmental
impact of the process [30]. In particular, setting up a DKR where only one product
is formed with complete substrate conversion constitutes an important milestone