Page 210 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 210
186 8 Racemizable Acyl Donors for Enzymatic Dynamic Kinetic Resolution
arene and, in consequence, this opens a narrow window of conditions where it
is plausible to attempt a DKR. In case of one-pot reactions, however, only poor
results have been obtained so far [41]; nonetheless, some success has been reported
in more complex systems exploiting compartmented reactors and immiscible
solvent mixtures, so that the racemization becomes physically separated from the
enzymatic resolution [42]. In the example, naproxen methyl ester was solubilized
in isooctane inside a stirred reactor, in which a coil of silicone tubing containing
solid NaOH dispersed in the same solvent was immersed, together with some
methanol and trimethylsilane. As the silicone rubber is highly hydrophobic, only
naproxen methyl ester could permeate the material, enter the tubing, and become
continuously racemized by sodium hydroxide, while the other additives prevent
hydrolysis. In the same reactor, an appropriate amount of Candida rugosa lipase
was dispersed into the isooctane phase together with some Tris–HCl buffer. When
the reactor was vigorously stirred and buffer was continuously pumped into the
mixture, the enzyme selectively hydrolyzed the ester in the water phase and the
acid product was sequestered. In the bottom of the reactor, a semi-impermeable
hydrophilic membrane operating in continuo extracted only the water phase, which
now contained the product. This clever setup permitted an easy separation of the
product and yielded naproxen with 96% ee at 60% conversion.
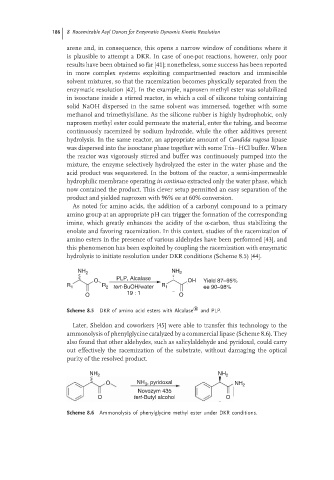
As noted for amino acids, the addition of a carbonyl compound to a primary
amino group at an appropriate pH can trigger the formation of the corresponding
imine, which greatly enhances the acidity of the α-carbon, thus stabilizing the
enolate and favoring racemization. In this context, studies of the racemization of
amino esters in the presence of various aldehydes have been performed [43], and
this phenomenon has been exploited by coupling the racemization with enzymatic
hydrolysis to initiate resolution under DKR conditions (Scheme 8.5) [44].
NH 2 NH 2
PLP, Alcalase
O OH Yield 87–95%
R 1 R 2 tert-BuOH/water R 1 ee 90–98%
O 19 : 1 O
Scheme 8.5 DKR of amino acid esters with Alcalase ® and PLP.
Later, Sheldon and coworkers [45] were able to transfer this technology to the
ammonolysis of phenylglycine catalyzed by a commercial lipase (Scheme 8.6). They
also found that other aldehydes, such as salicylaldehyde and pyridoxal, could carry
out effectively the racemization of the substrate, without damaging the optical
purity of the resolved product.
NH 2 NH 2
O NH , pyridoxal NH 2
3
Novozym 435
O tert-Butyl alcohol O
Scheme 8.6 Ammonolysis of phenylglycine methyl ester under DKR conditions.