Page 214 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 214
190 8 Racemizable Acyl Donors for Enzymatic Dynamic Kinetic Resolution
Resolution
COSPr B COSPr
Ar Ar
N O BH N O
Amano PS30
phosphate buffer
COSPr triethylamine
Ar Racemization Triton X-100 COOH
N O BH Ar
N O
(R)-XU305
COSPr COSPr
Ar Ar
N O N O
BH B
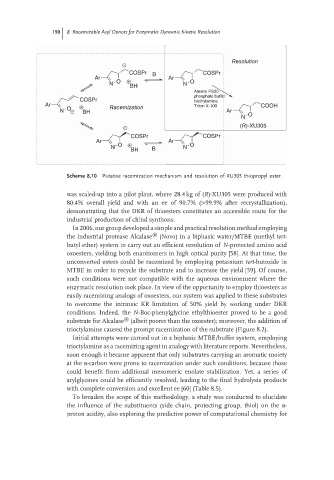
Scheme 8.10 Putative racemization mechanism and resolution of XU305 thiopropyl ester.
was scaled-up into a pilot plant, where 28.4 kg of (R)-XU305 were produced with
80.4% overall yield and with an ee of 90.7% (>99.9% after recrystallization),
demonstrating that the DKR of thioesters constitutes an accessible route for the
industrial production of chiral synthons.
In 2006, our group developed a simple and practical resolution method employing
the industrial protease Alcalase ® (Novo) in a biphasic water/MTBE (methyl tert-
butyl ether) system to carry out an efficient resolution of N-protected amino acid
oxoesters, yielding both enantiomers in high optical purity [58]. At that time, the
unconverted esters could be racemized by employing potassium tert-butoxide in
MTBE in order to recycle the substrate and to increase the yield [59]. Of course,
such conditions were not compatible with the aqueous environment where the
enzymatic resolution took place. In view of the opportunity to employ thioesters as
easily racemizing analogs of oxoesters, our system was applied to these substrates
to overcome the intrinsic KR limitation of 50% yield by working under DKR
conditions. Indeed, the N-Boc-phenylglycine ethylthioester proved to be a good
substrate for Alcalase ® (albeit poorer than the oxoester); moreover, the addition of
trioctylamine caused the prompt racemization of the substrate (Figure 8.2).
Initial attempts were carried out in a biphasic MTBE/buffer system, employing
trioctylamine as a racemizing agent in analogy with literature reports. Nevertheless,
soon enough it became apparent that only substrates carrying an aromatic moiety
at the α-carbon were prone to racemization under such conditions, because those
could benefit from additional mesomeric enolate stabilization. Yet, a series of
arylglycines could be efficiently resolved, leading to the final hydrolysis products
with complete conversion and excellent ee [60] (Table 8.5).
To broaden the scope of this methodology, a study was conducted to elucidate
the influence of the substituents (side chain, protecting group, thiol) on the α-
proton acidity, also exploring the predictive power of computational chemistry for