Page 324 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 324
300 14 Enzymatic Stereoselective Synthesis of -Amino Acids
and a 45% conversion was achieved when using a p-fluorophenyl-substituted
substrate.
CAL-B lipase has been applied to the resolution of some β-amino esters, by means
of N-acylation or transesterification [27]. Resolution using CAL-B is complicated
by the tendency of the enzyme to catalyze competing reactions at the amino and
ester functional groups. However, CAL-B has proved very useful for resolution by
means of β-lactam hydrolysis.
Lipase PS has also demonstrated excellent biocatalytic potential for use in the O-
acylation of hydroxymethylated β-lactam compounds. Lipase PS, much like CAL-B,
is capable of catalyzing N-acylation as well as reactions at the carboxylic group of
the β-amino ester [27].
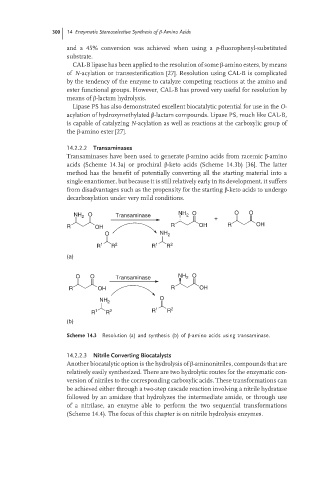
14.2.2.2 Transaminases
Transaminases have been used to generate β-amino acids from racemic β-amino
acids (Scheme 14.3a) or prochiral β-keto acids (Scheme 14.3b) [36]. The latter
method has the benefit of potentially converting all the starting material into a
single enantiomer, but because it is still relatively early in its development, it suffers
from disadvantages such as the propensity for the starting β-keto acids to undergo
decarboxylation under very mild conditions.
O NH 2 O O O
NH 2 Transaminase
+
R OH R OH R OH
O NH 2
R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2
(a)
O O Transaminase NH 2 O
R OH R OH
NH 2 O
R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2
(b)
Scheme 14.3 Resolution (a) and synthesis (b) of β-amino acids using transaminase.
14.2.2.3 Nitrile Converting Biocatalysts
Another biocatalytic option is the hydrolysis of β-aminonitriles, compounds that are
relatively easily synthesized. There are two hydrolytic routes for the enzymatic con-
version of nitriles to the corresponding carboxylic acids. These transformations can
be achieved either through a two-step cascade reaction involving a nitrile hydratase
followed by an amidase that hydrolyzes the intermediate amide, or through use
of a nitrilase, an enzyme able to perform the two sequential transformations
(Scheme 14.4). The focus of this chapter is on nitrile hydrolysis enzymes.