Page 51 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 51
2.2 Advances in Cofactor Regeneration 27
systems, that is, the xylose reductase-catalyzed reduction of xylose to xylitol and
the ADH-catalyzed synthesis of (R)-phenylethanol from the corresponding ketone
precursor. Both reactions were studied in membrane reactors under continuous
production conditions. Specifically, when applying a charged nanofiltration mem-
−1
brane in the production of xylitol, a remarkably high productivity (230 g l −1 d )
+
of this novel thermostable NADP -dependent PTDH was observed. The crystal
structure of thermostable PTDH variants with relaxed cofactor specificity has been
very recently solved and may provide further insights to elucidate the determinants
for substrate recognition [30].
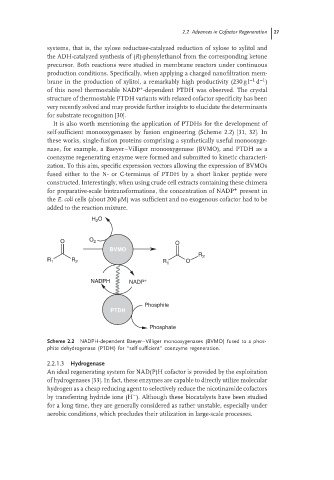
It is also worth mentioning the application of PTDHs for the development of
self-sufficient monooxygenases by fusion engineering (Scheme 2.2) [31, 32]. In
these works, single-fusion proteins comprising a synthetically useful monooxyge-
nase, for example, a Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenase (BVMO), and PTDH as a
coenzyme regenerating enzyme were formed and submitted to kinetic characteri-
zation. To this aim, specific expression vectors allowing the expression of BVMOs
fused either to the N- or C-terminus of PTDH by a short linker peptide were
constructed. Interestingly, when using crude cell extracts containing these chimera
+
for preparative-scale biotransformations, the concentration of NADP present in
the E. coli cells (about 200 μM) was sufficient and no exogenous cofactor had to be
added to the reaction mixture.
H O
2
O O 2 O
BVMO
R 2
R 1 R 2 O
R 1
NADPH NADP +
Phosphite
PTDH
Phosphate
Scheme 2.2 NADPH-dependent Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenases (BVMO) fused to a phos-
phite dehydrogenase (PTDH) for ‘‘self-sufficient’’ coenzyme regeneration.
2.2.1.3 Hydrogenase
An ideal regenerating system for NAD(P)H cofactor is provided by the exploitation
of hydrogenases [33]. In fact, these enzymes are capable to directly utilize molecular
hydrogen as a cheap reducing agent to selectively reduce the nicotinamide cofactors
−
by transferring hydride ions (H ). Although these biocatalysts have been studied
for a long time, they are generally considered as rather unstable, especially under
aerobic conditions, which precludes their utilization in large-scale processes.