Page 215 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 215
8.2 Material Preparation and Characterization 193
Biodegradable polymers as drug carriers have been extensively implemented in
biomedical fields [52]. They are not required to be separated from the body at
the end of the curing period since they can degrade into physiologically occurring
compounds that are simply released from the body [53, 54]. Their direct bene-
fits are ample, ranging from nontoxic degradation, constant drug release [7, 55]
to very minor effects on the adjacent tissues [56]. The popularity of using elec-
trospun nanofiber mats as effective carriers has dramatically increased in recent
years owing to their reasonable structural stability and higher drug-loading effi-
ciency [57]. In general, chemical and physical properties of different drug types
have impacts on the carrier capability of nanofiber mats [37, 58]. The drug release
can be controlled effectively by means of morphological modification, polymer
blending, drug dosage, and drug incorporation technique. This chapter aims to
develop a new drug carrier system based on electrospun PLA/PCL fibers to assist
the sustained drug release. Such fiber mats may promote a balanced crystallinity
level with the potential material merit for stable drug release. The relevant study is
inclined to the holistic investigation of the effects of PLA/PCL blend ratio, solvent
system, electrical conductivity of solution, solution viscosity, PCL concentration,
and molecular weight (MW) on fiber diameter and degree of crystallinity as two
important factors for the effective control of drug release.
8.2
Material Preparation and Characterization
−1
PLA3051D pellets (MW = 93 500 g mol ) were supplied by Nature Works,
−1
USA. Low-molecular-weight (LMW) PCL (MW = 33 000 g mol )was pur-
chased from Daicel Chemical Industries Ltd, Japan while high-molecular-weight
−1
(HMW) PCL (MW = 80 000 g mol ) and tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH)
−1
(chemical structure: C H N O ⋅HCl and MW = 480.9 g mol ) were obtained
22 24 2 8
from Sigma-Aldrich Ltd, Australia. In addition, the solvents used, such as
dichloromethane (DCM), dimethylformamide (DMF), chloroform (CHCl ),
3
acetone, and methanol (MeOH), as well as phosphate buffer solution (PBS), as
a drug release medium were also supplied by Sigma-Aldrich Ltd, Australia and
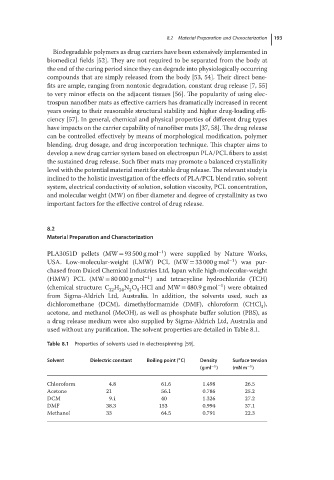
used without any purification. The solvent properties are detailed in Table 8.1.
Table 8.1 Properties of solvents used in electrospinning [59].
∘
Solvent Dielectric constant Boiling point ( C) Density Surface tension
−1
−1
(g ml ) (mN m )
Chloroform 4.8 61.6 1.498 26.5
Acetone 21 56.1 0.786 25.2
DCM 9.1 40 1.326 27.2
DMF 38.3 153 0.994 37.1
Methanol 33 64.5 0.791 22.3