Page 223 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 223
8.3 Morphological Observations 201
80 600
Fibre diameter (chloroform/methanol)
70 Fibre diameter (chloroform/acetone)
Solution viscosity (chloroform/methanol) 500
60 Solution viscosity (chloroform/acetone) 400
Solution viscosity (cP) 40 300 Fibre diameter (nm)
50
30
20 200
100
10
0 0
(1/0) (3/1) (1/1)
PLA/PCL blend ratio
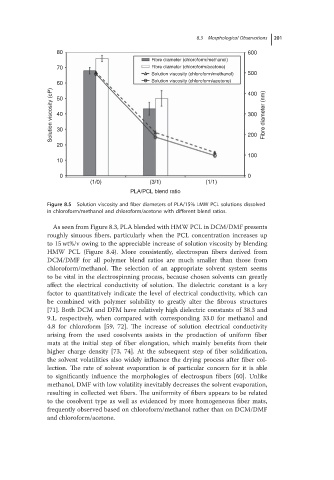
Figure 8.5 Solution viscosity and fiber diameters of PLA/15% LMW PCL solutions dissolved
in chloroform/methanol and chloroform/acetone with different blend ratios.
As seen from Figure 8.3, PLA blended with HMW PCL in DCM/DMF presents
roughly sinuous fibers, particularly when the PCL concentration increases up
to 15 wt%/v owing to the appreciable increase of solution viscosity by blending
HMW PCL (Figure 8.4). More consistently, electrospun fibers derived from
DCM/DMF for all polymer blend ratios are much smaller than those from
chloroform/methanol. The selection of an appropriate solvent system seems
to be vital in the electrospinning process, because chosen solvents can greatly
affect the electrical conductivity of solution. The dielectric constant is a key
factor to quantitatively indicate the level of electrical conductivity, which can
be combined with polymer solubility to greatly alter the fibrous structures
[71]. Both DCM and DFM have relatively high dielectric constants of 38.3 and
9.1, respectively, when compared with corresponding 33.0 for methanol and
4.8 for chloroform [59, 72]. The increase of solution electrical conductivity
arising from the used cosolvents assists in the production of uniform fiber
mats at the initial step of fiber elongation, which mainly benefits from their
higher charge density [73, 74]. At the subsequent step of fiber solidification,
the solvent volatilities also widely influence the drying process after fiber col-
lection. The rate of solvent evaporation is of particular concern for it is able
to significantly influence the morphologies of electrospun fibers [60]. Unlike
methanol, DMF with low volatility inevitably decreases the solvent evaporation,
resulting in collected wet fibers. The uniformity of fibers appears to be related
to the cosolvent type as well as evidenced by more homogeneous fiber mats,
frequently observed based on chloroform/methanol rather than on DCM/DMF
and chloroform/acetone.