Page 225 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 225
8.4 Crystalline Structures 203
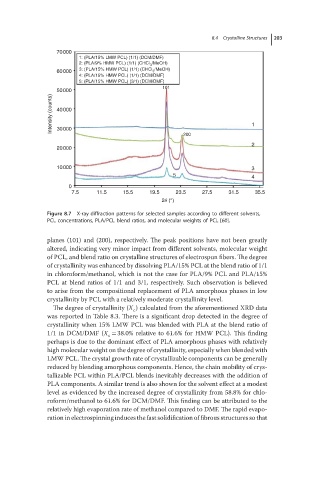
70000
1: (PLA/15% LMW PCL) (1/1) (DCM/DMF)
2: (PLA/9% HMW PCL) (1/1) (CHCl /MeOH)
3
60000 3: (PLA/15% HMW PCL) (1/1) (CHCl /MeOH)
3
4: (PLA/15% HMW PCL) (1/1) (DCM/DMF)
5: (PLA/15% HMW PCL) (3/1) (DCM/DMF)
101
50000
Intensity (counts) 40000
30000
200 1
2
20000
10000 3
5 4
0
7.5 11.5 15.5 19.5 23.5 27.5 31.5 35.5
2θ (°)
Figure 8.7 X-ray diffraction patterns for selected samples according to different solvents,
PCL concentrations, PLA/PCL blend ratios, and molecular weights of PCL [60].
planes (101) and (200), respectively. The peak positions have not been greatly
altered, indicating very minor impact from different solvents, molecular weight
of PCL, and blend ratio on crystalline structures of electrospun fibers. The degree
of crystallinity was enhanced by dissolving PLA/15% PCL at the blend ratio of 1/1
in chloroform/methanol, which is not the case for PLA/9% PCL and PLA/15%
PCL at blend ratios of 1/1 and 3/1, respectively. Such observation is believed
to arise from the compositional replacement of PLA amorphous phases in low
crystallinity by PCL with a relatively moderate crystallinity level.
The degree of crystallinity (X ) calculated from the aforementioned XRD data
c
was reported in Table 8.3. There is a significant drop detected in the degree of
crystallinity when 15% LMW PCL was blended with PLA at the blend ratio of
1/1 in DCM/DMF (X = 38.0% relative to 61.6% for HMW PCL). This finding
c
perhaps is due to the dominant effect of PLA amorphous phases with relatively
high molecular weight on the degree of crystallinity, especially when blended with
LMW PCL. The crystal growth rate of crystallizable components can be generally
reduced by blending amorphous components. Hence, the chain mobility of crys-
tallizable PCL within PLA/PCL blends inevitably decreases with the addition of
PLA components. A similar trend is also shown for the solvent effect at a modest
level as evidenced by the increased degree of crystallinity from 58.8% for chlo-
roform/methanol to 61.6% for DCM/DMF. This finding can be attributed to the
relatively high evaporation rate of methanol compared to DMF. The rapid evapo-
ration in electrospinning induces the fast solidification of fibrous structures so that