Page 226 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 226
204 8 Systematic Development of Electrospun PLA/PCL Fiber Hybrid Mats
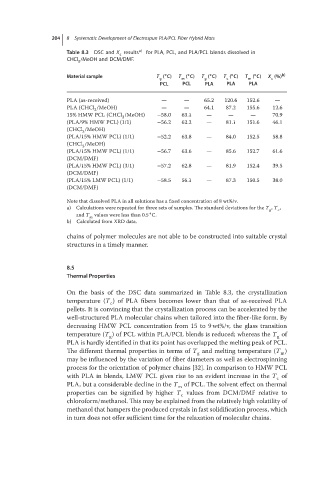
Table 8.3 DSC and X results a) for PLA, PCL, and PLA/PCL blends dissolved in
c
CHCl /MeOH and DCM/DMF.
3
∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ b)
Material sample T ( C) T ( C) T ( C) T ( C) T ( C) X (%)
g m g c m c
PCL PCL PLA PLA PLA
PLA (as-received) — — 65.2 120.6 152.6 —
PLA (CHCl /MeOH) — — 64.1 87.2 155.6 12.6
3
15% HMW PCL (CHCl /MeOH) −58.0 63.1 — — — 70.9
3
(PLA/9% HMW PCL) (1/1) −56.2 62.2 — 81.1 151.6 46.1
(CHCl /MeOH)
3
(PLA/15% HMW PCL) (1/1) −52.2 63.8 — 84.0 152.5 58.8
(CHCl /MeOH)
3
(PLA/15% HMW PCL) (1/1) −56.7 63.6 — 85.6 152.7 61.6
(DCM/DMF)
(PLA/15% HMW PCL) (3/1) −57.2 62.8 — 81.9 152.4 39.5
(DCM/DMF)
(PLA/15% LMW PCL) (1/1) −58.5 56.1 — 87.3 150.5 38.0
(DCM/DMF)
Note that dissolved PLA in all solutions has a fixed concentration of 8 wt%/v.
a) Calculations were repeated for three sets of samples. The standard deviations for the T , T , c
g
∘
and T m values were less than 0.5 C.
b) Calculated from XRD data.
chains of polymer molecules are not able to be constructed into suitable crystal
structures in a timely manner.
8.5
Thermal Properties
On the basis of the DSC data summarized in Table 8.3, the crystallization
temperature (T ) of PLA fibers becomes lower than that of as-received PLA
c
pellets. It is convincing that the crystallization process can be accelerated by the
well-structured PLA molecular chains when tailored into the fiber-like form. By
decreasing HMW PCL concentration from 15 to 9 wt%/v, the glass transition
temperature (T )ofPCL within PLA/PCLblendsisreduced;whereasthe T of
g
g
PLA is hardly identified in that its point has overlapped the melting peak of PCL.
The different thermal properties in terms of T and melting temperature (T )
m
g
may be influenced by the variation of fiber diameters as well as electrospinning
process for the orientation of polymer chains [32]. In comparison to HMW PCL
with PLA in blends, LMW PCL gives rise to an evident increase in the T of
c
PLA, but a considerable decline in the T of PCL. The solvent effect on thermal
m
properties can be signified by higher T values from DCM/DMFrelativeto
c
chloroform/methanol. This may be explained from the relatively high volatility of
methanol that hampers the produced crystals in fast solidification process, which
in turn does not offer sufficient time for the relaxation of molecular chains.