Page 28 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 28
6 1 Biodegradable Polyesters: Synthesis, Properties, Applications
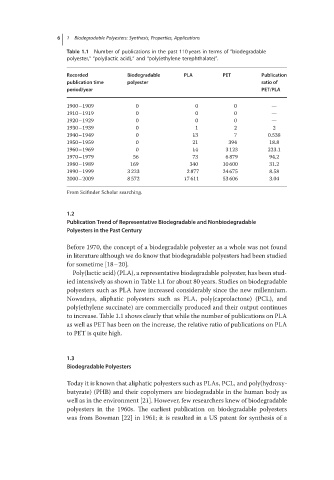
Table 1.1 Number of publications in the past 110 years in terms of “biodegradable
polyester,” “poly(lactic acid),” and “poly(ethylene terephthalate)”.
Recorded Biodegradable PLA PET Publication
publication time polyester ratio of
period/year PET/PLA
1900–1909 0 0 0 —
1910–1919 0 0 0 —
1920–1929 0 0 0 —
1930–1939 0 1 2 2
1940–1949 0 13 7 0.538
1950–1959 0 21 394 18.8
1960–1969 0 14 3 123 223.1
1970–1979 56 73 6 879 94.2
1980–1989 169 340 10 600 31.2
1990–1999 3 223 2 877 24 675 8.58
2000–2009 8 572 17 611 53 606 3.04
From Scifinder Scholar searching.
1.2
Publication Trend of Representative Biodegradable and Nonbiodegradable
Polyesters in the Past Century
Before 1970, the concept of a biodegradable polyester as a whole was not found
in literature although we do know that biodegradable polyesters had been studied
for sometime [18–20].
Poly(lactic acid) (PLA), a representative biodegradable polyester, has been stud-
ied intensively as shown in Table 1.1 for about 80 years. Studies on biodegradable
polyesters such as PLA have increased considerably since the new millennium.
Nowadays, aliphatic polyesters such as PLA, poly(caprolactone) (PCL), and
poly(ethylene succinate) are commercially produced and their output continues
to increase. Table 1.1 shows clearly that while the number of publications on PLA
as well as PET has been on the increase, the relative ratio of publications on PLA
to PET is quite high.
1.3
Biodegradable Polyesters
Today it is known that aliphatic polyesters such as PLAs, PCL, and poly(hydroxy-
butyrate) (PHB) and their copolymers are biodegradable in the human body as
well as in the environment [21]. However, few researchers knew of biodegradable
polyesters in the 1960s. The earliest publication on biodegradable polyesters
was from Bowman [22] in 1961; it is resulted in a US patent for synthesis of a