Page 198 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 198
Processing of Vegetable Oils as Biodiesel and Engine Performance 181
C-1 and C-3 are magnetically nonequivalent, due to four double doublets,
which are observed in the spectra. But 2-MG, on the other hand, are
symmetrical, and C-1 and C-3 methylene protons are magnetically equiva-
lent and appear as a multiplate.
6.2.3 Enzymatic transesterification
of vegetable oils
Enzymatic transesterification of TG by lipases (3.1.1.3) is a good alter-
native over a chemical process due to its eco-friendly, selective nature
and low temperature requirement. Lipases break down the TAG into
FFA and glycerol that exhibits maximum activity at the oil–water inter-
face. Under low-water conditions, the hydrolysis reaction is reversible,
i.e., the ester bond is synthesized rather than hydrolyzed. Scientists
are interested in the development of lipase applications to the inter-
esterification reactions of vegetable oils for production of biodiesel.
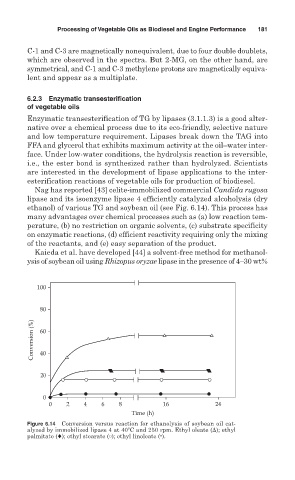
Nag has reported [43] celite-immobilized commercial Candida rugosa
lipase and its isoenzyme lipase 4 efficiently catalyzed alcoholysis (dry
ethanol) of various TG and soybean oil (see Fig. 6.14). This process has
many advantages over chemical processes such as (a) low reaction tem-
perature, (b) no restriction on organic solvents, (c) substrate specificity
on enzymatic reactions, (d) efficient reactivity requiring only the mixing
of the reactants, and (e) easy separation of the product.
Kaieda et al. have developed [44] a solvent-free method for methanol-
ysis of soybean oil using Rhizopus oryzae lipase in the presence of 4–30 wt%
100
80
Conversion (%) 60
40
20
0
0 2 4 6 8 16 24
Time (h)
Figure 6.14 Conversion versus reaction for ethanolysis of soybean oil cat-
alyzed by immobilized lipase 4 at 40 C and 250 rpm. Ethyl oleate ( ); ethyl
palmitate (♦); ethyl stearate ( ); ethyl linoleate ( •).