Page 194 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 194
Processing of Vegetable Oils as Biodiesel and Engine Performance 177
0.05
Diesel
20% K blend
20% J blend
0.04
20% P blend
K-Karanja
J-Jatropha
0.03 P-Putranjiva
CO (%)
0.02
0.01
0.00
0.0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4
Brake power (kW)
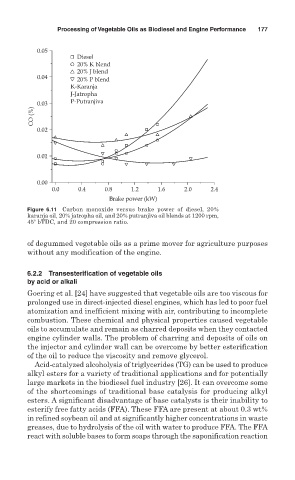
Figure 6.11 Carbon monoxide versus brake power of diesel, 20%
karanja oil, 20% jatropha oil, and 20% putranjiva oil blends at 1200 rpm,
45 bTDC, and 20 compression ratio.
of degummed vegetable oils as a prime mover for agriculture purposes
without any modification of the engine.
6.2.2 Transesterification of vegetable oils
by acid or alkali
Goering et al. [24] have suggested that vegetable oils are too viscous for
prolonged use in direct-injected diesel engines, which has led to poor fuel
atomization and inefficient mixing with air, contributing to incomplete
combustion. These chemical and physical properties caused vegetable
oils to accumulate and remain as charred deposits when they contacted
engine cylinder walls. The problem of charring and deposits of oils on
the injector and cylinder wall can be overcome by better esterification
of the oil to reduce the viscosity and remove glycerol.
Acid-catalyzed alcoholysis of triglycerides (TG) can be used to produce
alkyl esters for a variety of traditional applications and for potentially
large markets in the biodiesel fuel industry [26]. It can overcome some
of the shortcomings of traditional base catalysis for producing alkyl
esters. A significant disadvantage of base catalysts is their inability to
esterify free fatty acids (FFA). These FFA are present at about 0.3 wt%
in refined soybean oil and at significantly higher concentrations in waste
greases, due to hydrolysis of the oil with water to produce FFA. The FFA
react with soluble bases to form soaps through the saponification reaction