Page 257 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 257
236 Chapter Eight
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 ppm
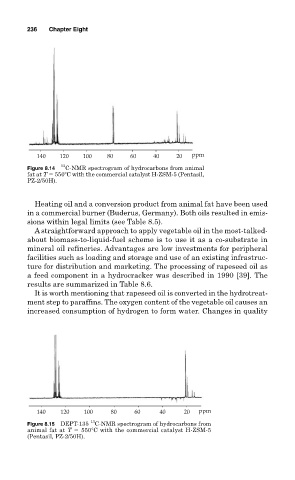
13
Figure 8.14 C-NMR spectrogram of hydrocarbons from animal
fat at T 550 C with the commercial catalyst H-ZSM-5 (Pentasil,
PZ-2/50H).
Heating oil and a conversion product from animal fat have been used
in a commercial burner (Buderus, Germany). Both oils resulted in emis-
sions within legal limits (see Table 8.5).
A straightforward approach to apply vegetable oil in the most-talked-
about biomass-to-liquid-fuel scheme is to use it as a co-substrate in
mineral oil refineries. Advantages are low investments for peripheral
facilities such as loading and storage and use of an existing infrastruc-
ture for distribution and marketing. The processing of rapeseed oil as
a feed component in a hydrocracker was described in 1990 [39]. The
results are summarized in Table 8.6.
It is worth mentioning that rapeseed oil is converted in the hydrotreat-
ment step to paraffins. The oxygen content of the vegetable oil causes an
increased consumption of hydrogen to form water. Changes in quality
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 ppm
Figure 8.15 DEPT-135 13 C-NMR spectrogram of hydrocarbons from
animal fat at T 550 C with the commercial catalyst H-ZSM-5
(Pentasil, PZ-2/50H).