Page 68 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 68
Photosynthetic Plants as Renewable Energy Sources 51
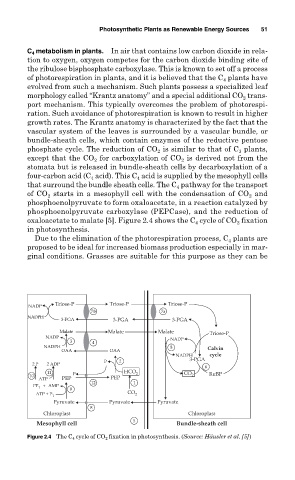
C 4 metabolism in plants. In air that contains low carbon dioxide in rela-
tion to oxygen, oxygen competes for the carbon dioxide binding site of
the ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. This is known to set off a process
of photorespiration in plants, and it is believed that the C plants have
4
evolved from such a mechanism. Such plants possess a specialized leaf
morphology called “Krantz anatomy” and a special additional CO 2 trans-
port mechanism. This typically overcomes the problem of photorespi-
ration. Such avoidance of photorespiration is known to result in higher
growth rates. The Krantz anatomy is characterized by the fact that the
vascular system of the leaves is surrounded by a vascular bundle, or
bundle-sheath cells, which contain enzymes of the reductive pentose
is similar to that of C plants,
phosphate cycle. The reduction of CO 2 3
except that the CO for carboxylation of CO is derived not from the
2
2
stomata but is released in bundle-sheath cells by decarboxylation of a
four-carbon acid (C acid). This C acid is supplied by the mesophyll cells
4
4
that surround the bundle sheath cells. The C pathway for the transport
4
of CO starts in a mesophyll cell with the condensation of CO and
2
2
phosphoenolpyruvate to form oxaloacetate, in a reaction catalyzed by
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPCase), and the reduction of
oxaloacetate to malate [5]. Figure 2.4 shows the C cycle of CO fixation
4
2
in photosynthesis.
Due to the elimination of the photorespiration process, C plants are
4
proposed to be ideal for increased biomass production especially in mar-
ginal conditions. Grasses are suitable for this purpose as they can be
Triose-P Triose-P Triose-P
NADP
7b 7a
NADPH
3-PGA 3-PGA 3-PGA
Malate Malate Malate Triose-P
NADP NADP
3 4
NADPH 5 Calvin
OAA OAA
NADPH cycle
3-PGA
P 2
2 P 2 ADP
6
11 HCO RuBP
10 P PEP 2 CO 2
ATP PEP
12 1
PP 1 + AMP
9
ATP + P 1 CO 2
Pyruvate Pyruvate Pyruvate
8
Chloroplast Chloroplast
5
Mesophyll cell Bundle-sheath cell
Figure 2.4 The C 4 cycle of CO 2 fixation in photosynthesis. (Source: Häusler et al. [5])