Page 157 - Biofuels for a More Sustainable Future
P. 157
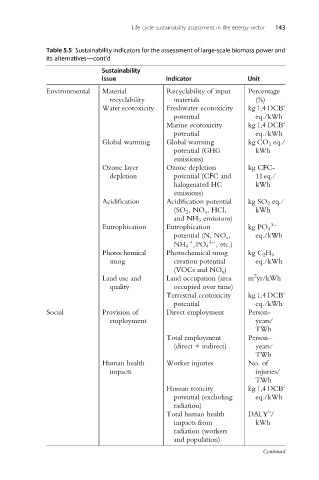
Life cycle sustainability assessment in the energy sector 143
Table 5.5 Sustainability indicators for the assessment of large-scale biomass power and
its alternatives—cont’d
Sustainability
Issue Indicator Unit
Environmental Material Recyclability of input Percentage
recyclability materials (%)
Water ecotoxicity Freshwater ecotoxicity kg 1,4 DCB a
potential eq./kWh
Marine ecotoxicity kg 1,4 DCB a
potential eq./kWh
Global warming Global warming kg CO 2 eq./
potential (GHG kWh
emissions)
Ozone layer Ozone depletion kg CFC-
depletion potential (CFC and 11eq./
halogenated HC kWh
emissions)
Acidification Acidification potential kg SO 2 eq./
(SO 2 ,NO x , HCl, kWh
and NH 3 emissions)
Eutrophication Eutrophication kg PO 4 3
potential (N, NO x , eq./kWh
+ 3
NH 4 ,PO 4 , etc.)
Photochemical Photochemical smog kg C 2 H 4
smog creation potential eq./kWh
(VOCs and NO x )
2
Land use and Land occupation (area m yr/kWh
quality occupied over time)
Terrestrial ecotoxicity kg 1,4 DCB a
potential eq./kWh
Social Provision of Direct employment Person-
employment years/
TWh
Total employment Person-
(direct + indirect) years/
TWh
Human health Worker injuries No. of
impacts injuries/
TWh
Human toxicity kg 1,4 DCB a
potential (excluding eq./kWh
radiation)
b
Total human health DALY /
impacts from kWh
radiation (workers
and population)
Continued