Page 30 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 30
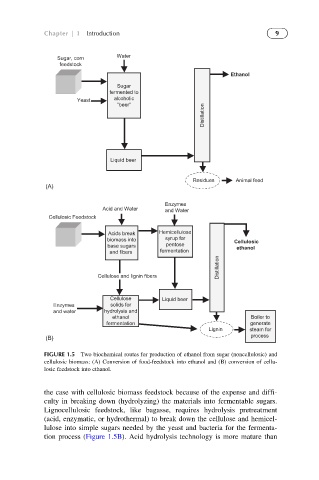
Chapter | 1 Introduction 9
Water
Sugar, corn
feedstock
Ethanol
Sugar
fermented to
alcoholic
Yeast
“beer”
Distillation
Liquid beer
Residues Animal feed
(A)
Enzymes
Acid and Water and Water
Cellulosic Feedstock
Acids break Hemicellulose
biomass into syrup for Cellulosic
base sugars pentose ethanol
and fibers fermentation
Distillation
Cellulose and lignin fibers
Cellulose Liquid beer
Enzymes solids for
and water hydrolysis and
ethanol Boiler to
fermentation generate
Lignin steam for
(B) process
FIGURE 1.5 Two biochemical routes for production of ethanol from sugar (noncellulosic) and
cellulosic biomass: (A) Conversion of food-feedstock into ethanol and (B) conversion of cellu-
losic feedstock into ethanol.
the case with cellulosic biomass feedstock because of the expense and diffi-
culty in breaking down (hydrolyzing) the materials into fermentable sugars.
Lignocellulosic feedstock, like bagasse, requires hydrolysis pretreatment
(acid, enzymatic, or hydrothermal) to break down the cellulose and hemicel-
lulose into simple sugars needed by the yeast and bacteria for the fermenta-
tion process (Figure 1.5B). Acid hydrolysis technology is more mature than