Page 342 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 342
BIOPOLYMERS 319
13.3 SPECIFIC POLYMERS
13.3.1 Water-Soluble Polymers
Water-soluble polymers are used for a variety of applications. They can be adsorbed or covalently
bound to surfaces to make them more hydrophilic, less thrombogenic, and more lubricious. They can
be used as protective coatings to prevent damage during surgery. Hyaluronic acid solutions are used in
ophthalmic surgery to prevent damage to the cornea and iris. They can be cross-linked to form hydro-
gels for soft tissue replacement and for drug delivery applications. There are numerous water-soluble
biopolymers. The polymers discussed below are some of the more common and useful examples.
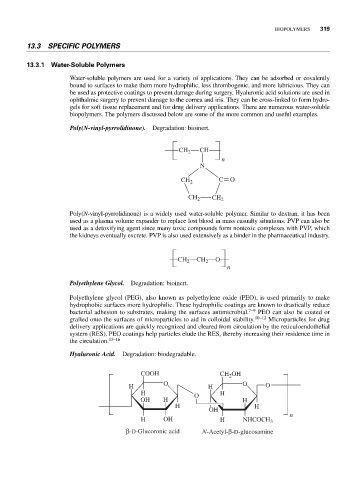
Poly(N-vinyl-pyrrolidinone). Degradation: bioinert.
CH 2 CH
n
N
CH 2 C O
CH 2 CH 2
Poly(N-vinyl-pyrrolidinone) is a widely used water-soluble polymer. Similar to dextran, it has been
used as a plasma volume expander to replace lost blood in mass casualty situations. PVP can also be
used as a detoxifying agent since many toxic compounds form nontoxic complexes with PVP, which
the kidneys eventually excrete. PVP is also used extensively as a binder in the pharmaceutical industry.
CH 2 CH 2 O
n
Polyethylene Glycol. Degradation: bioinert.
Polyethylene glycol (PEG), also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO), is used primarily to make
hydrophobic surfaces more hydrophilic. These hydrophilic coatings are known to drastically reduce
bacterial adhesion to substrates, making the surfaces antimicrobial. 7–9 PEO can also be coated or
grafted onto the surfaces of microparticles to aid in colloidal stability. 10–12 Microparticles for drug
delivery applications are quickly recognized and cleared from circulation by the reticuloendothelial
system (RES). PEO coatings help particles elude the RES, thereby increasing their residence time in
the circulation. 13–16
Hyaluronic Acid. Degradation: biodegradable.
COOH CH 2 OH
O O
H H O
H O H
OH H H
H H
OH
n
H OH H NHCOCH 3
β-D-Glucoronic acid N-Acetyl-β-D-glucosamine