Page 49 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 49
26 BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS ANALYSIS
1.6.2 Fuzzy Mechanics
Virtual reality (VR) is gaining importance in every discipline, including medicine and surgery. VR is
a computer-generated pseudo space that looks, feels, hears, and smells real, and fully immerses the
subject. Potential applications of VR include medical education and training, patient education, VR-
enhanced rehabilitation exercises, VR-induced biofeedback therapy and teletherapy, VR-aided emer-
gency medicine, and VR surgical simulations, etc. Surgical simulations in VR environment can aid
the surgeon in planning and determining the optimal surgical procedure for a given patient, and also
can aid in medical education. Song and Reddy (1995) have demonstrated the proof of concept for
tissue cutting in VR environment. They have developed a technique for cutting in VR using interac-
tive moving node finite element models controlled by user-exerted forces on instrumented pseudo
cutting tool held by the user. In Song and Reddy’s system, the user (surgeon) holds the instrumented
wand (instrumented pseudo tool) and manipulates the tool. The forces exerted by the wand (on a
table) together with the orientation and location of the wand are measured and fed to a finite element
model of the tissue and the deformations are calculated to update the model geometry. Cutting takes
place if the force exerted is larger than the critical force (computed from local tissue properties) at
the node. Otherwise, tissue simply deforms depending on the applied force. However, finite element
models require significant amount of computational time and may not be suitable for cutting large
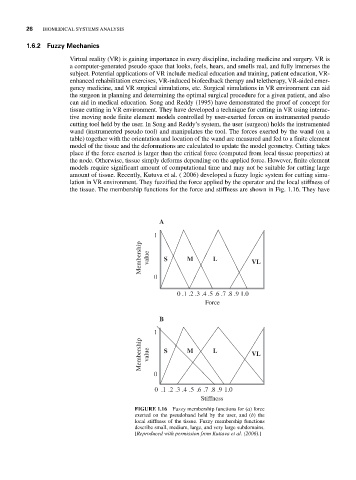
amount of tissue. Recently, Kutuva et al. ( 2006) developed a fuzzy logic system for cutting simu-
lation in VR environment. They fuzzified the force applied by the operator and the local stiffness of
the tissue. The membership functions for the force and stiffness are shown in Fig. 1.16. They have
A
1
Membership value S M L VL
0
0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1.0
Force
B
1
Membership value S M L VL
0
0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1.0
Stiffness
FIGURE 1.16 Fuzzy membership functions for (a) force
exerted on the pseudohand held by the user, and (b) the
local stiffness of the tissue. Fuzzy membership functions
describe small, medium, large, and very large subdomains.
[Reproduced with permission from Kuttava et al. (2006).]