Page 194 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 194
DESIGN OF CONTROLLED-RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS 173
The rate of drug pumped out of the device dM/dt can be expressed as
dM ⎛ dV ⎞
= C (6.19)
dt ⎝ dt ⎠
where C is the drug concentration. As long as the osmotically active agent provides the constant
osmotic pressure, the delivery system will release the drug at a zero-order. The zero-order delivery
rate can be expressed as
⎛ dM ⎞ = AK π C
⎝ dt ⎠ z h s (6.20)
where π s is osmotic pressure generated by saturated solution and all other symbols are the same as
described earlier.
6.9 ION-EXCHANGE RESINS
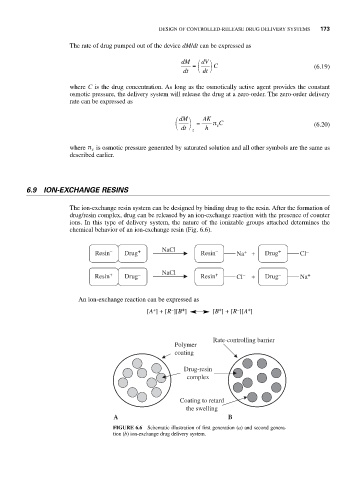
The ion-exchange resin system can be designed by binding drug to the resin. After the formation of
drug/resin complex, drug can be released by an ion-exchange reaction with the presence of counter
ions. In this type of delivery system, the nature of the ionizable groups attached determines the
chemical behavior of an ion-exchange resin (Fig. 6.6).
Resin – Drug + NaCl Resin – Na + + Drug + Cl –
Resin + Drug – NaCl Resin + Cl – + Drug – Na +
An ion-exchange reaction can be expressed as
−
−
+
+
+
+
[A ] + [R ][B ] [B ] + [R ][A ]
Rate-controlling barrier
Polymer
coating
Drug-resin
complex
Coating to retard
the swelling
A B
FIGURE 6.6 Schematic illustration of first generation (a) and second genera-
tion (b) ion-exchange drug delivery system.