Page 62 - Biomimetics : Biologically Inspired Technologies
P. 62
Bar-Cohen : Biomimetics: Biologically Inspired Technologies DK3163_c002 Final Proof page 48 21.9.2005 11:39am
48 Biomimetics: Biologically Inspired Technologies
(a) (b)
8 5
7
4
6 5
Sarcomere Length (µm) 4 3 Myosin Filament Length (µm) 3 2
2
1
1
(96) (56) (33) (37) (52) (6) (61) (14) (23) (8) (36) (6)
0 0
All Fast muscles Flight muscles Crawl muscles All Fast muscles Flight muscles Crawl muscles
Slow muscles
Slow muscles
Run/Swim muscles
Run/Swim muscles
(c) 6 5 (d) Sarcomere Morphology
Ratio thin / thick filament number (Actin / myosin) 4 3 2
1
sarc
(50) (21) (29) (9) (35) (6) L L myo
0
All Fast muscles Flight muscles Crawl muscles
Slow muscles
Run/Swim muscles
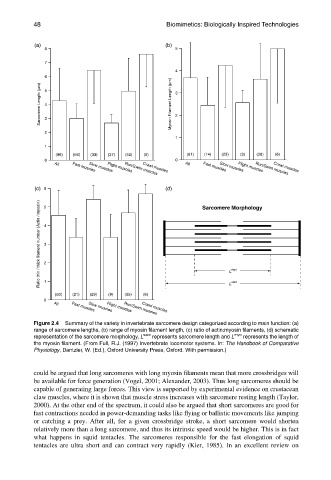
Figure 2.4 Summary of the variety in invertebrate sarcomere design categorized according to main function: (a)
range of sarcomere lengths, (b) range of myosin filament length, (c) ratio of actin:myosin filaments, (d) schematic
representation of the sarcomere morphology, L sarc represents sarcomere length and L myo represents the length of
the myosin filament. (From Full, R.J. (1997) Invertebrate locomotor systems. In: The Handbook of Comparative
Physiology, Dantzler, W. (Ed.), Oxford University Press, Oxford. With permission.)
could be argued that long sarcomeres with long myosin filaments mean that more crossbridges will
be available for force generation (Vogel, 2001; Alexander, 2003). Thus long sarcomeres should be
capable of generating large forces. This view is supported by experimental evidence on crustacean
claw muscles, where it is shown that muscle stress increases with sarcomere resting length (Taylor,
2000). At the other end of the spectrum, it could also be argued that short sarcomeres are good for
fast contractions needed in power-demanding tasks like flying or ballistic movements like jumping
or catching a prey. After all, for a given crossbridge stroke, a short sarcomere would shorten
relatively more than a long sarcomere, and thus its intrinsic speed would be higher. This is in fact
what happens in squid tentacles. The sarcomeres responsible for the fast elongation of squid
tentacles are ultra short and can contract very rapidly (Kier, 1985). In an excellent review on