Page 419 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 419
396 Cha pte r F o u r tee n
O OH
COOMe
O
OMe
OH
HO
O
OH OH HO
HO HO OH MeO
Tyrosol Hydroxytyrosol Elenolic acid Syringic acid
O COOH CH=CHCOOH
HO OH
OH
COOH
HO
OH OH
OH OH OH HO
Gallic acid Protocatecuic acid Caffeic acid Gentisic acid
OMe
OMe
OMe
HO COOH HO COOH HO COOH
HO COOH
p-Hydroxyphenylacetic Homovanillic acid Cinnamic acid Ferulic acid
OH
OMe O
COOH COOH COOH
COOH HO
HO
OH OMe OH
p-Coumaric acid o-Cumaric acid Sinapinic acid Shikimic acid
OH
OH HO
OH
OH OH
HO O
HO O HO O
OH OH
OH O OH OH
Quercetin Catechin Epicatechin
H OH HO
OMe
HO C
C O CH
HO COOH HO COOH H HO 3
OH O
p-Hydroxybenzoic Vanillic acid Resveratrol Hydroxytyrosol acetate
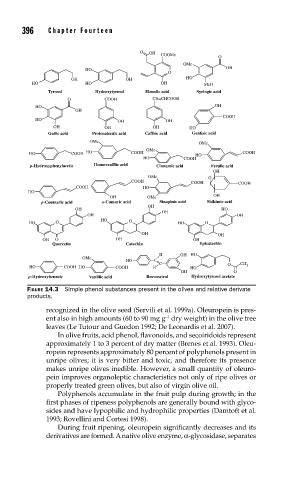
FIGURE 14.3 Simple phenol substances present in the olives and relative derivate
products.
recognized in the olive seed (Servili et al. 1999a). Oleuropein is pres-
–1
ent also in high amounts (60 to 90 mg g dry weight) in the olive tree
leaves (Le Tutour and Guedon 1992; De Leonardis et al. 2007).
In olive fruits, acid phenol, flavonoids, and secoiridoids represent
approximately 1 to 3 percent of dry matter (Brenes et al. 1993). Oleu-
ropein represents approximately 80 percent of polyphenols present in
unripe olives; it is very bitter and toxic, and therefore its presence
makes unripe olives inedible. However, a small quantity of oleuro-
pein improves organoleptic characteristics not only of ripe olives or
properly treated green olives, but also of virgin olive oil.
Polyphenols accumulate in the fruit pulp during growth; in the
first phases of ripeness polyphenols are generally bound with glyco-
sides and have lypophilic and hydrophilic properties (Damtoft et al.
1993; Rovellini and Cortesi 1998).
During fruit ripening, oleuropein significantly decreases and its
derivatives are formed. A native olive enzyme, α-glycosidase, separates