Page 420 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 420
Phenolic Substances fr om Olives & Olive Mill Pr oducts 397
R 1 HO
OR 2
O O C O O
HO H HO O COOMe
H 3 C O
O
O-Glucose
CH 3
OGlu
R 1 = OH R 2 = Me oleuropein
R 1 = OH R 2 = OH demethyloleuropein Oleuropein
R 1 = H R 2 = Me ligstroside
O O O O
HO COOH HO COOMe
O O
OGlu OGlu
Ligstroside
Demethyloleuropein
R 3
OH
HO
OH
HO O-mannose R 1 O O
HO O O O OH
OH O
R 2
OH O
Verbascoside
R 1 R 2 R 3
Apigenin 7-glucoside 4 Glu H H
Luteolin 7-glucoside 3 Glu H OH
Rutin 1 H O-Rha-Glu OH
OH 4 3 COOCH 3
2 6
1 8 1′′ 5′′ 6′′ O 7 5 4 3
O O
7 HO OH O 9 O
2′′ HO 3′′ 4′′ 8 1
1′ 5′ 6′ OH
10 O O
OH 3′ OH
2′ 4′
Nüzhenide OH
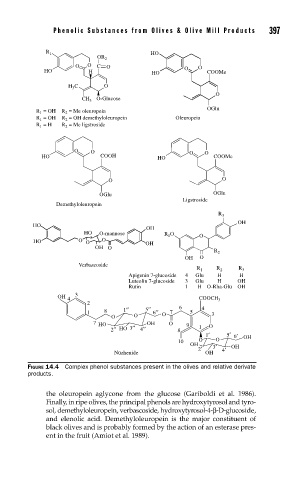
FIGURE 14.4 Complex phenol substances present in the olives and relative derivate
products.
the oleuropein aglycone from the glucose (Gariboldi et al. 1986).
Finally, in ripe olives, the principal phenols are hydroxytyrosol and tyro-
sol, demethyloleuropein, verbascoside, hydroxytyrosol-4-β-D-glucoside,
and elenolic acid. Demethyloleuropein is the major constituent of
black olives and is probably formed by the action of an esterase pres-
ent in the fruit (Amiot et al. 1989).