Page 64 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 64
Biosystems Analysis and Optimization 45
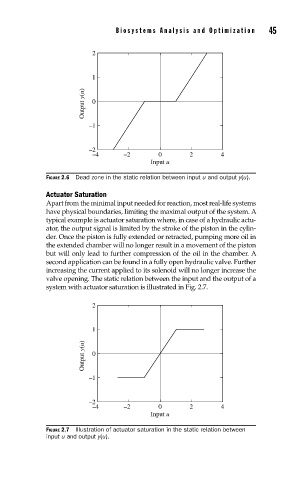
2
1
y(u)
Output 0
–1
–2
–4 –2 0 2 4
Input u
FIGURE 2.6 Dead zone in the static relation between input u and output y(u).
Actuator Saturation
Apart from the minimal input needed for reaction, most real-life systems
have physical boundaries, limiting the maximal output of the system. A
typical example is actuator saturation where, in case of a hydraulic actu-
ator, the output signal is limited by the stroke of the piston in the cylin-
der. Once the piston is fully extended or retracted, pumping more oil in
the extended chamber will no longer result in a movement of the piston
but will only lead to further compression of the oil in the chamber. A
second application can be found in a fully open hydraulic valve. Further
increasing the current applied to its solenoid will no longer increase the
valve opening. The static relation between the input and the output of a
system with actuator saturation is illustrated in Fig. 2.7.
2
1
y(u) 0
Output
–1
–2
–4 –2 0 2 4
Input u
FIGURE 2.7 Illustration of actuator saturation in the static relation between
input u and output y(u).