Page 105 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 105
90 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
burned hydrocarbons, begin to show up. cleaning, to identify any deviations from baseline
If this information is not available, then levels. Since stack temperature usually increases
general information can be used based on infor- with firing rate and excess air, make your com-
mation from typical minimum oxygen settings parisons at similar boiler operating conditions.
in similar boilers. The following general infor- If previous information is not available or if
mation on minimum excess oxygen is based on a temperatures seem excessive, the following graph
large number of boiler tests and is applicable to (Fig 9.2) can be used for general estimates. Tem-
high firing rates. As firing rate decreases burner perature readings to measure boiler performance
performance falls off and more excess air may be must be taken before economizers or air heaters
needed for some burners. cool down the flue gases but overall performance
is judged from the temperature after these units.
Target Oxygen Levels
• Natural gas boilers, 0.5% to 3% INSPECTING YOUR BOILER
• Liquid fuels, 2% to 4%
• Pulverized coal, 3% to 6% Boiler components that you should inspect
• Stoker fired coal, 4% to 8% before conducting efficiency tests include burn-
ers, combustion controls and furnace. Typical
things to look for are shown below (Figure 9.3
STACK TEMPERATURE through Figure 9.5). Consult your boiler manu-
facturer for a more complete list appropriate to
Stack temperature measurements are an the specific equipment in your plant.
easy and effective means for monitoring boiler
tube cleanliness and the general effectiveness Oil burners
of the heat exchange process in a boiler. Exist- • Make sure the atomizer is suitable for your
ing temperatures can be compared to values ob- present firing conditions; for the type of oil
tained during start up or after maintenance and being burned and burner geometry.
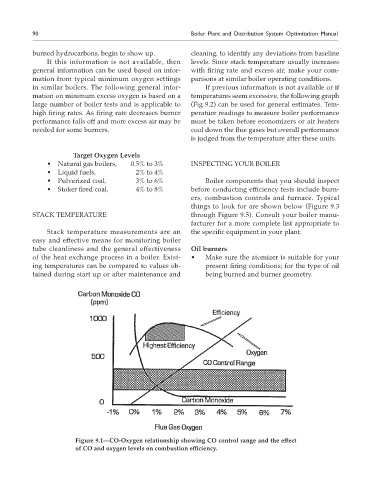
Figure 9.1—CO-Oxygen relationship showing CO control range and the effect
of CO and oxygen levels on combustion efficiency.