Page 29 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 29
14 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
the steam pressure on a boiler not connected to a set at the wide open position. In the absence of
header system, the steam line should be warmed a non-return valve, the boiler stop valve should
up along with the boiler by the operation of drain be opened slowly when the pressure in the boiler
valves to remove condensation and create the de- and header are approximately equal.
sired flow of warming steam.
In bringing a boiler on the line with other
boilers on a header system, certain precautions WARM-UP
are necessary to avoid water hammer and exces-
sive temperature gradients in the piping. Ade- During the period when steam pressure is
quate drainage and warming of the piping will initially being raised, the boiler, especially the
eliminate the risk of water hammer. The judicious boiler drum which is fabricated from thick metal,
use of bypass valves around main header valves can experience some unusual and possibly dam-
will avoid steep temperature gradients. Header aging stresses. To avoid thermal stress, tempera-
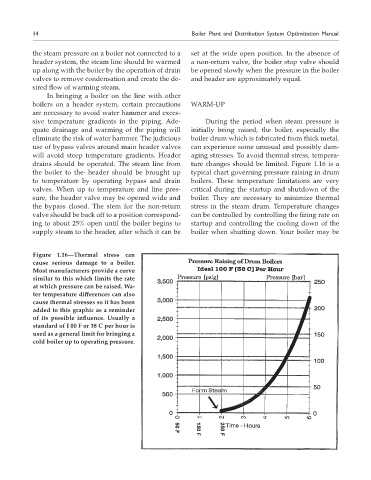
drains should be operated. The steam line from ture changes should be limited. Figure 1.16 is a
the boiler to the· header should be brought up typical chart governing pressure raising in drum
to temperature by operating bypass and drain boilers. These temperature limitations are very
valves. When up to temperature and line pres- critical during the startup and shutdown of the
sure, the header valve may be opened wide and boiler. They are necessary to minimize thermal
the bypass closed. The stem for the non-return stress in the steam drum. Temperature changes
valve should be back off to a position correspond- can be controlled by controlling the firing rate on
ing to about 25% open until the boiler begins to startup and controlling the cooling down of the
supply steam to the header, after which it can be boiler when shutting down. Your boiler may be
Figure 1.16—Thermal stress can
cause serious damage to a boiler.
Most manufacturers provide a curve
similar to this which limits the rate
at which pressure can be raised. Wa-
ter temperature differences can also
cause thermal stresses so it has been
added to this graphic as a reminder
of its possible influence. Usually a
standard of I 00 F or 38 C per hour is
used as a general limit for bringing a
cold boiler up to operating pressure.