Page 25 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 25
10 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
NATURAL CIRCULATION IN BOILER TUBES 1. Receive feedwater from the economizer and
distribute it to the downcomers.
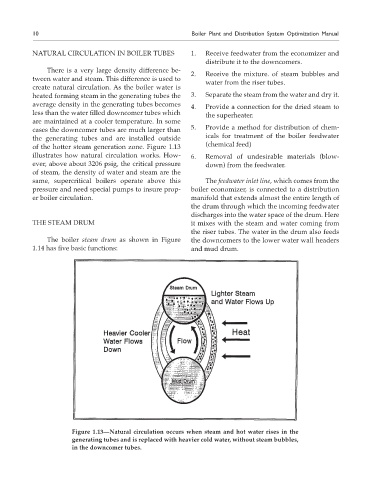
There is a very large density difference be-
2. Receive the mixture. of steam bubbles and
tween water and steam. This difference is used to
water from the riser tubes.
create natural circulation. As the boiler water is
heated forming steam in the generating tubes the 3. Separate the steam from the water and dry it.
average density in the generating tubes becomes 4. Provide a connection for the dried steam to
less than the water filled downcomer tubes which the superheater.
are maintained at a cooler temperature. In some
cases the downcomer tubes are much larger than 5. Provide a method for distribution of chem-
the generating tubes and are installed outside icals for treatment of the boiler feedwater
of the hotter steam generation zone. Figure 1.13 (chemical feed)
illustrates how natural circulation works. How- 6. Removal of undesirable materials (blow-
ever, above about 3206 psig, the critical pressure down) from the feedwater.
of steam, the density of water and steam are the
same, supercritical boilers operate above this The feedwater inlet line, which comes from the
pressure and need special pumps to insure prop- boiler economizer, is connected to a distribution
er boiler circulation. manifold that extends almost the entire length of
the drum through which the incoming feedwater
discharges into the water space of the drum. Here
THE STEAM DRUM it mixes with the steam and water coming from
the riser tubes. The water in the drum also feeds
The boiler steam drum as shown in Figure the downcomers to the lower water wall headers
1.14 has five basic functions: and mud drum.
Figure 1.13—Natural circulation occurs when steam and hot water rises in the
generating tubes and is replaced with heavier cold water, without steam bubbles,
in the downcomer tubes.