Page 22 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 22
Boiler Plant Orientation 7
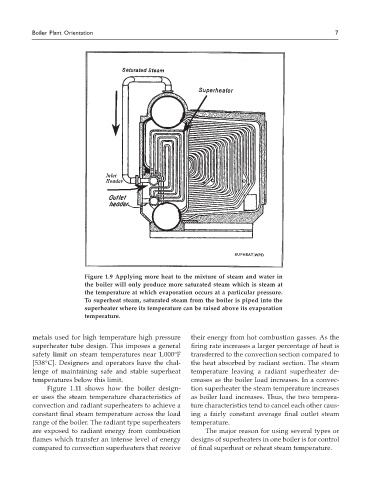
Figure 1.9 Applying more heat to the mixture of steam and water in
the boiler will only produce more saturated steam which is steam at
the temperature at which evaporation occurs at a particular pressure.
To superheat steam, saturated steam from the boiler is piped into the
superheater where its temperature can be raised above its evaporation
temperature.
metals used for high temperature high pressure their energy from hot combustion gasses. As the
superheater tube design. This imposes a general firing rate increases a larger percentage of heat is
safety limit on steam temperatures near 1,000°F transferred to the convection section compared to
[538°C]. Designers and operators have the chal- the heat absorbed by radiant section. The steam
lenge of maintaining safe and stable superheat temperature leaving a radiant superheater de-
temperatures below this limit. creases as the boiler load increases. In a convec-
Figure 1.11 shows how the boiler design- tion superheater the steam temperature increases
er uses the steam temperature characteristics of as boiler load increases. Thus, the two tempera-
convection and radiant superheaters to achieve a ture characteristics tend to cancel each other caus-
constant final steam temperature across the load ing a fairly constant average final outlet steam
range of the boiler. The radiant type superheaters temperature.
are exposed to radiant energy from combustion The major reason for using several types or
flames which transfer an intense level of energy designs of superheaters in one boiler is for control
compared to convection superheaters that receive of final superheat or reheat steam temperature.