Page 92 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 92
The Control of Boilers 77
melting point for boiler steel. The pressure PARALLEL POSITIONING CONTROL
vessel is normally kept cool by the water and
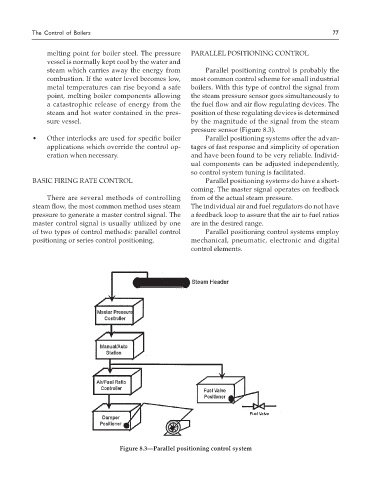
steam which carries away the energy from Parallel positioning control is probably the
combustion. If the water level becomes low, most common control scheme for small industrial
metal temperatures can rise beyond a safe boilers. With this type of control the signal from
point, melting boiler components allowing the steam pressure sensor goes simultaneously to
a catastrophic release of energy from the the fuel flow and air flow regulating devices. The
steam and hot water contained in the pres- position of these regulating devices is determined
sure vessel. by the magnitude of the signal from the steam
pressure sensor (Figure 8.3).
• Other interlocks are used for specific boiler Parallel positioning systems offer the advan-
applications which override the control op- tages of fast response and simplicity of operation
eration when necessary. and have been found to be very reliable. Individ-
ual components can be adjusted independently,
so control system tuning is facilitated.
BASIC FIRING RATE CONTROL Parallel positioning systems do have a short-
coming. The master signal operates on feedback
There are several methods of controlling from of the actual steam pressure.
steam flow, the most common method uses steam The individual air and fuel regulators do not have
pressure to generate a master control signal. The a feedback loop to assure that the air to fuel ratios
master control signal is usually utilized by one are in the desired range.
of two types of control methods: parallel control Parallel positioning control systems employ
positioning or series control positioning. mechanical, pneumatic, electronic and digital
control elements.
Figure 8.3—Parallel positioning control system