Page 155 - Build Your Own Quadcopter_ Power Up Your Designs with the Parallax Elev-8
P. 155
134 Bu il d Y o ur O w n Q u a d c o p t e r
Specification Description
Frequency 2400 to 2483.5 MHz divided into eighty 1 MHz channels (the
extra bandwidth is allotted to edge guard bands)
Maximum power 1000 mW US, 100 mW Europe, and 10 mW/MHz Japan
Minimum power 1 mW
Rx sensitivity -80 dB
Table 6.2 Some Key R/C DSSS Specifications
DSSS is also the same modulation technique specified for use in the IEEE standard 802.11,
commonly known as Wi-Fi. Some key R/C DSSS specifications are shown in Table 6.2.
As DSSS is fairly complex, I will attempt to describe and discuss only the essential
features that are applicable to the R/C field. The essence of DSSS is to represent primary
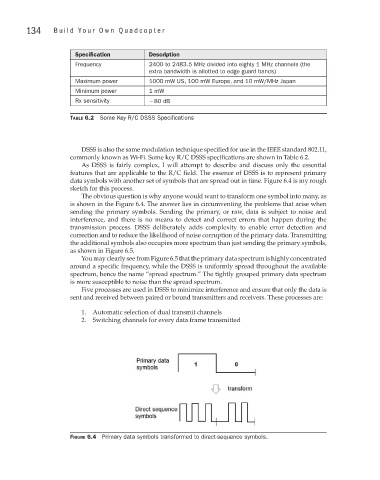
data symbols with another set of symbols that are spread out in time. Figure 6.4 is my rough
sketch for this process.
The obvious question is why anyone would want to transform one symbol into many, as
is shown in the Figure 6.4. The answer lies in circumventing the problems that arise when
sending the primary symbols. Sending the primary, or raw, data is subject to noise and
interference, and there is no means to detect and correct errors that happen during the
transmission process. DSSS deliberately adds complexity to enable error detection and
correction and to reduce the likelihood of noise corruption of the primary data. Transmitting
the additional symbols also occupies more spectrum than just sending the primary symbols,
as shown in Figure 6.5.
You may clearly see from Figure 6.5 that the primary data spectrum is highly concentrated
around a specific frequency, while the DSSS is uniformly spread throughout the available
spectrum, hence the name “spread spectrum.” The tightly grouped primary data spectrum
is more susceptible to noise than the spread spectrum.
Five processes are used in DSSS to minimize interference and ensure that only the data is
sent and received between paired or bound transmitters and receivers. These processes are:
1. Automatic selection of dual transmit channels
2. Switching channels for every data frame transmitted
Figure 6.4 Primary data symbols transformed to direct-sequence symbols.