Page 163 - Build Your Own Transistor Radios a Hobbyists Guide to High-Performance and Low-Powered Radio Circuits
P. 163
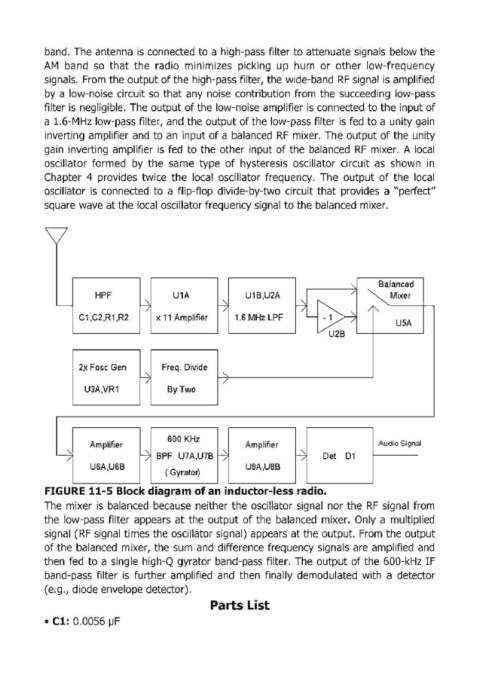
band. The antenna is connected to a high-pass filter to attenuate signals below the
AM band so that the radio minimizes picking up hum or other low-frequency
signals. From the output of the high-pass filter, the wide-band RF signal is amplified
by a low-noise circuit so that any noise contribution from the succeeding low-pass
filter is negligible. The output of the low-noise amplifier is connected to the input of
a 1.6-MHz low-pass filter, and the output of the low-pass filter is fed to a unity gain
inverting amplifier and to an input of a balanced RF mixer. The output of the unity
gain inverting amplifier is fed to the other input of the balanced RF mixer. A local
oscillator formed by the same type of hysteresis oscillator circuit as shown in
Chapter 4 provides twice the local oscillator frequency. The output of the local
oscillator is connected to a flip-flop divide-by-two circuit that provides a "perfect"
square wave at the local oscillator frequency signal to the balanced mixer.
Mixer
HPF U1A U1B,U2A , " Balanced
/
-7 / rj L-~
~ r..::
/
C1 ,C2,R1 ,R2 x 11 Amplifier 1.S MHz LPF "
U5A
U2B
2x Fasc Gen Freq. Divide
-7 "
/
U3A,VR1 By Two
SOO KHz
Amplifier Amplifier Audio Signal
y ...:; BPF U7A,u7B r..:: H Det 01
/ / / /
USA,USB USA,USB
( Gyrator)
. . .
FIGURE 11-5 Block diagram of an tnductor-Iess radio.
The mixer is balanced because neither the oscillator signal nor the RF signal from
the low-pass filter appears at the output of the balanced mixer. Only a multiplied
signal (RF signal times the oscillator signal) appears at the output. From the output
of the balanced mixer, the sum and difference frequency signals are amplified and
then fed to a single high-Q gyrator band-pass filter. The output of the 600-kHz IF
band-pass filter is further amplified and then finally demodulated with a detector
(e.g., diode envelope detector).
Parts List
• Cl: 0.0056 IJF