Page 125 - Calculus Demystified
P. 125
CHAPTER 4
The Integral
112
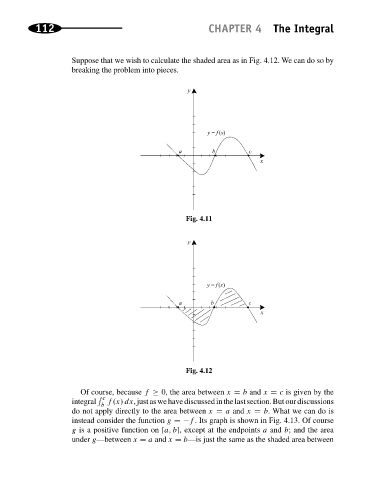
Suppose that we wish to calculate the shaded area as in Fig. 4.12. We can do so by
breaking the problem into pieces.
Fig. 4.11
Fig. 4.12
Of course, because f ≥ 0, the area between x = b and x = c is given by the
c
integral f(x) dx,justaswehavediscussedinthelastsection.Butourdiscussions
b
do not apply directly to the area between x = a and x = b. What we can do is
instead consider the function g =−f . Its graph is shown in Fig. 4.13. Of course
g is a positive function on [a, b], except at the endpoints a and b; and the area
under g—between x = a and x = b—is just the same as the shaded area between