Page 130 - Calculus Demystified
P. 130
The Integral
CHAPTER 4
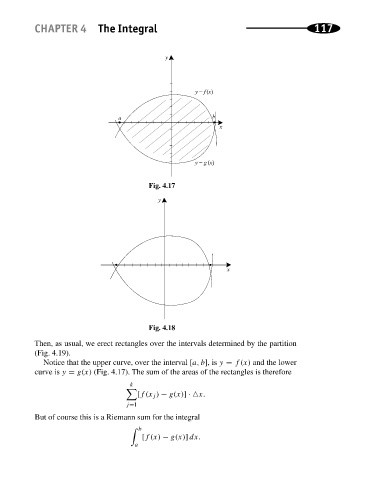
Fig. 4.17 117
Fig. 4.18
Then, as usual, we erect rectangles over the intervals determined by the partition
(Fig. 4.19).
Notice that the upper curve, over the interval [a, b],is y = f(x) and the lower
curve is y = g(x) (Fig. 4.17). The sum of the areas of the rectangles is therefore
k
[f(x j ) − g(x)]· x.
j=1
But of course this is a Riemann sum for the integral
b
[f(x) − g(x)] dx.
a