Page 558 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 558
THBAP 9/19/03 7:29 PM Page 546
546 CAM DESIGN HANDBOOK
where C is a constant.
In addition it may be noted that with V, the vertex, the distance
GV = FV.
Construction:
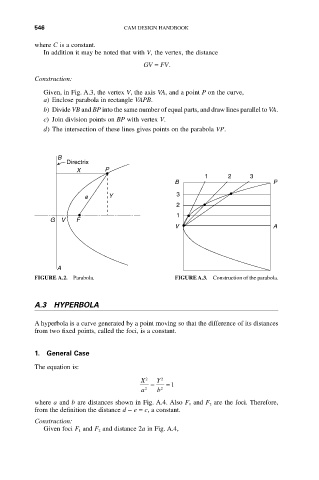
Given, in Fig. A.3, the vertex V, the axis VA, and a point P on the curve,
a) Enclose parabola in rectangle VAPB.
b) Divide VB and BP into the same number of equal parts, and draw lines parallel to VA.
c) Join division points on BP with vertex V.
d) The intersection of these lines gives points on the parabola VP.
B
Directrix
X P
1 2 3
B P
e Y 3
2
1
G V F
V A
A
FIGURE A.2. Parabola. FIGURE A.3. Construction of the parabola.
A.3 HYPERBOLA
A hyperbola is a curve generated by a point moving so that the difference of its distances
from two fixed points, called the foci, is a constant.
1. General Case
The equation is:
X 2 Y 2
- = 1
a 2 b 2
where a and b are distances shown in Fig. A.4. Also F 1 and F 2 are the foci. Therefore,
from the definition the distance d - e = c, a constant.
Construction:
Given foci F 1 and F 2 and distance 2a in Fig. A.4,