Page 560 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 560
THBAP 9/19/03 7:29 PM Page 548
548 CAM DESIGN HANDBOOK
The equation becomes
XY = C.
Construction:
Given OX and OY as asymptotes of the curve and any point P on the curve,
a) Draw PA and PB.
b) Mark any points 1, 2, and 3, etc., on PB, and through these points draw lines par-
allel to OX, and also lines through O.
c) From the intersection with line AP extended draw lines parallel to OA.
d) The intersections give the hyperbola.
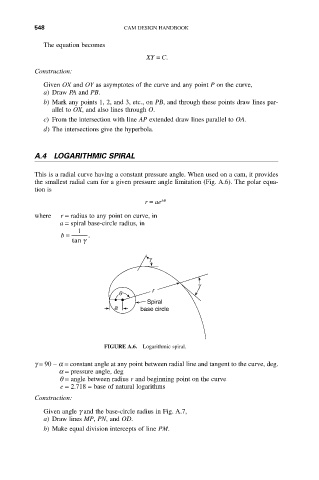
A.4 LOGARITHMIC SPIRAL
This is a radial curve having a constant pressure angle. When used on a cam, it provides
the smallest radial cam for a given pressure angle limitation (Fig. A.6). The polar equa-
tion is
r = ae bq
where r = radius to any point on curve, in
a = spiral base-circle radius, in
1
b = .
tan g
g
g
q r
Spiral
a base circle
FIGURE A.6. Logarithmic spiral.
g = 90 - a = constant angle at any point between radial line and tangent to the curve, deg.
a = pressure angle, deg
q = angle between radius r and beginning point on the curve
e = 2.718 = base of natural logarithms
Construction:
Given angle g and the base-circle radius in Fig. A.7,
a) Draw lines MP, PN, and OD.
b) Make equal division intercepts of line PM.