Page 39 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 39
32 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
(A) CNT/Teflon film (B) Fast
collector bobbin
Spinning
Detached drawable
CNT array
Teflon/CNT roll
bobbin
Solid Support
Teflon film on a
Teflon film bobbin
delivering bobbin
(C)
CNT Film
Glass slide
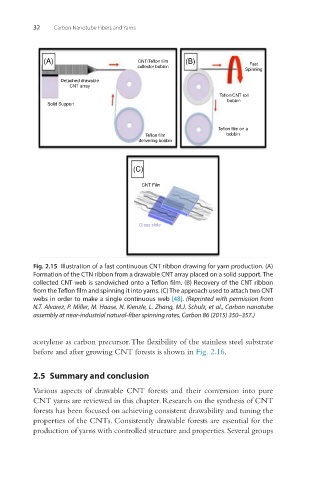
Fig. 2.15 Illustration of a fast continuous CNT ribbon drawing for yarn production. (A)
Formation of the CTN ribbon from a drawable CNT array placed on a solid support. The
collected CNT web is sandwiched onto a Teflon film. (B) Recovery of the CNT ribbon
from the Teflon film and spinning it into yarns. (C) The approach used to attach two CNT
webs in order to make a single continuous web [48]. (Reprinted with permission from
N.T. Alvarez, P. Miller, M. Haase, N. Kienzle, L. Zhang, M.J. Schulz, et al., Carbon nanotube
assembly at near-industrial natural-fiber spinning rates, Carbon 86 (2015) 350–357.)
acetylene as carbon precursor. The flexibility of the stainless steel substrate
before and after growing CNT forests is shown in Fig. 2.16.
2.5 Summary and conclusion
Various aspects of drawable CNT forests and their conversion into pure
CNT yarns are reviewed in this chapter. Research on the synthesis of CNT
forests has been focused on achieving consistent drawability and tuning the
properties of the CNTs. Consistently drawable forests are essential for the
production of yarns with controlled structure and properties. Several groups