Page 45 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 45
38 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
CNT fibers can be produced from substrate-CVD grown CNT arrays
(covered in Chapter 2), or from aerogel-like CNT sock in floating catalyst
method. The floating catalyst method could continuously produce CNT
fibers. This chapter will focus on the floating catalyst method. The essen-
tial synthesis parameters will be discussed. This is followed by the CNT
fiber spinning process. The CNT fiber structure and properties will also be
covered.
3.2 Floating catalyst synthesis of CNTs
The synthesis of CNTs precedes the formation of CNT fibers. The floating
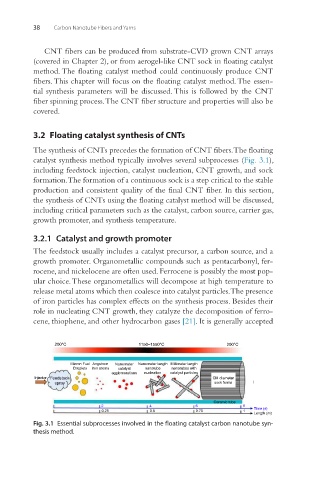
catalyst synthesis method typically involves several subprocesses (Fig. 3.1),
including feedstock injection, catalyst nucleation, CNT growth, and sock
formation. The formation of a continuous sock is a step critical to the stable
production and consistent quality of the final CNT fiber. In this section,
the synthesis of CNTs using the floating catalyst method will be discussed,
including critical parameters such as the catalyst, carbon source, carrier gas,
growth promoter, and synthesis temperature.
3.2.1 Catalyst and growth promoter
The feedstock usually includes a catalyst precursor, a carbon source, and a
growth promoter. Organometallic compounds such as pentacarbonyl, fer-
rocene, and nickelocene are often used. Ferrocene is possibly the most pop-
ular choice. These organometallics will decompose at high temperature to
release metal atoms which then coalesce into catalyst particles. The presence
of iron particles has complex effects on the synthesis process. Besides their
role in nucleating CNT growth, they catalyze the decomposition of ferro-
cene, thiophene, and other hydrocarbon gases [21]. It is generally accepted
200°C 1150–1550°C 200°C
Micron Fuel Angstrom Nanometer Nanometer length Millimeter length
Droplets Iron atoms catalyst nanotube nanotubes with
agglomerations nucleation catalyst particles
Injector Feedstock CM diameter
spray sock forms
Ceramic tube
2 4 6 8
0.25 0.5 0.75 1 Time (s)
Length (m)
Fig. 3.1 Essential subprocesses involved in the floating catalyst carbon nanotube syn-
thesis method.